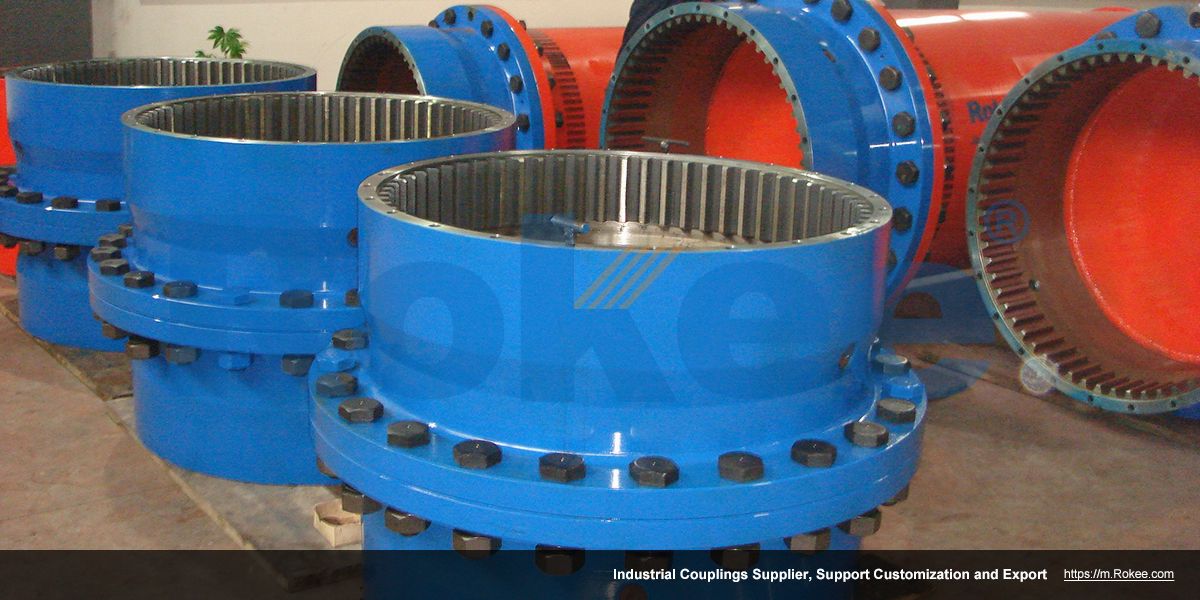
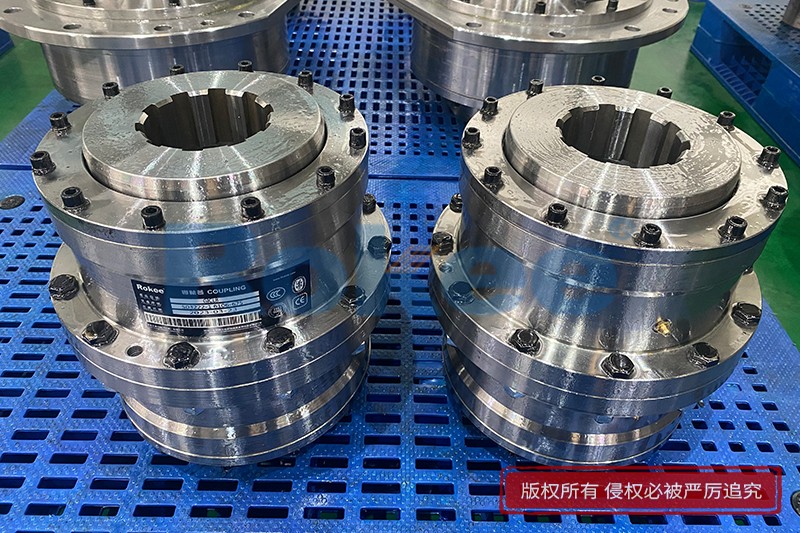
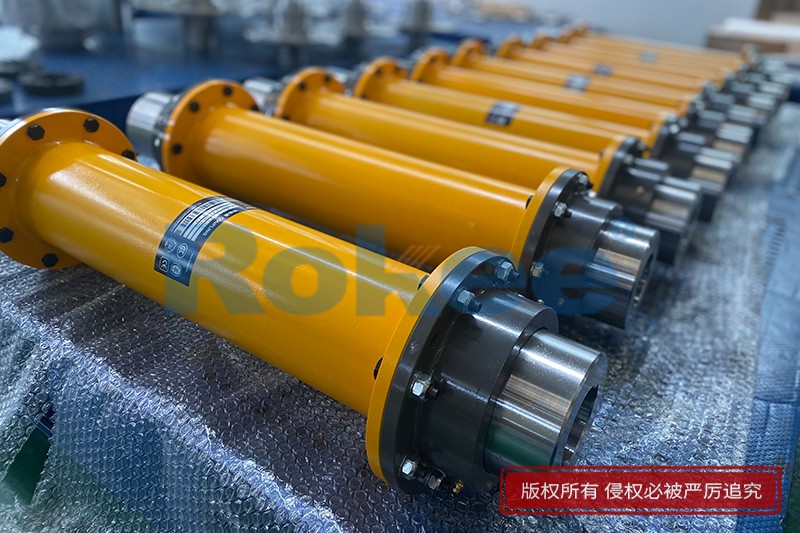
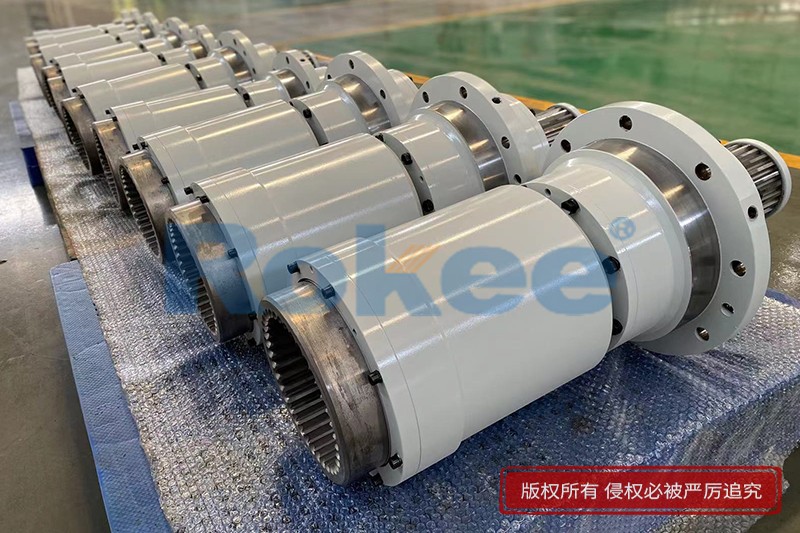
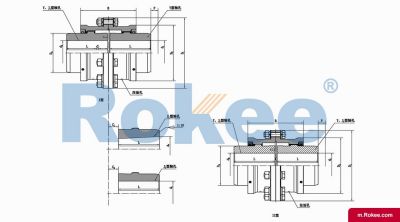
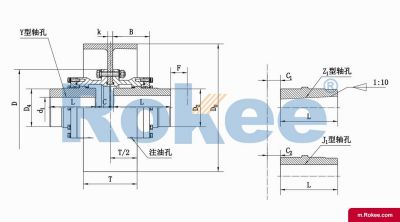
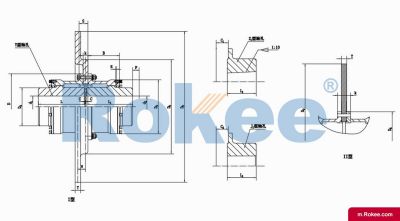
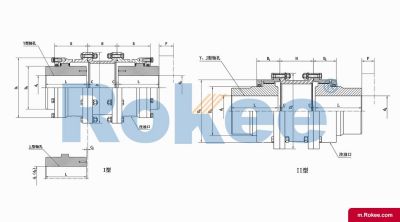
Rokee is a chinese Curved-tooth Gear Couplings Manufacturer, provide Curved-tooth Gear Couplings processing and customization services, Over the years, with excellent quality, we have been continuously providing many coupling products of various categories and uses complying with multiple standards and a full range of services, from the Curved-tooth Gear Couplings selection to final installation and operation, for the industry fields of ferrous metallurgy, nuclear power, gas turbine, wind power, ropeway construction, lifting transportation, general equipment, etc. We strictly comply with quality system requirements and implement the whole process control to become a reliable and trustworthy partner of customers.
Providing customers with better Curved-tooth Gear Couplings is always our driving force. Our aim is to transmit power for you and generate value for both of us. We look forward to joining you and becoming your partner for common progress.
-
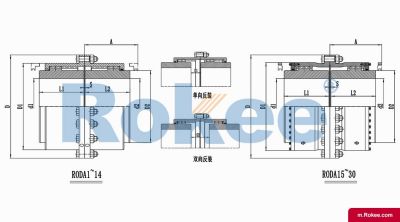
RODA Basic Drum Gear Coupling
The RODA Drum Gear Coupling is the basic type of ROD series coupling, suitable for most situations where the compensation of transmission distance and motion position does not require special increase.View More -
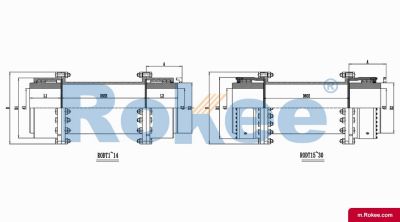
RODT Drum Gear Coupling With Intermediate Tube
The RODT Drum Gear Coupling is an extended type of ROD series coupling, suitable for increasing transmission distance.View More -
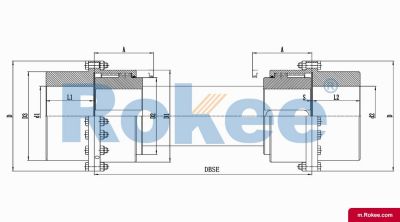
RODX Drum Gear Coupling With Intermediate Shaft
RODX Drum Gear Coupling is an extended type of ROD series coupling with a floating shaft design in the middle, suitable for increasing transmission distance.View More -
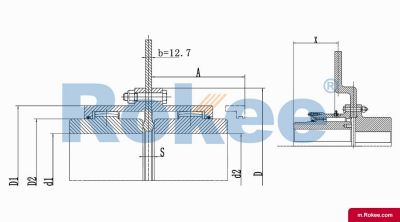
RODP Drum Gear Coupling With Brake Disc
The RODP Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with a brake disc, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with disc brakes.View More -
RODF Drum Gear Coupling With Split Brake Discs
The RODF Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with split brake discs, suitable for transmission situations where there is braking demand and the braking position changes when used in conjunction with disc brakes.View More -
RODW Drum Gear Coupling With Brake Wheel
The RODW Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with brake wheels, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with wheel brakes.View More -
RODU Drum Gear Coupling With Brake Wheel
The RODU Drum Gear Coupling is another type of ROD series coupling with brake wheels, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with wheel brakes and applied to one end of the axle, achieving smoother and more reliable braking performance.View More -
RODV Vertical Installation Drum Gear Coupling
The RODV Drum Gear Coupling is a vertical installation type of the ROD series coupling, suitable for transmission situations that require vertical transmission torque.View More -
RODM Torsion Protection Drum Gear Coupling
The RODM Drum Gear Coupling is a torque setting form of the ROD series coupling. By adjusting relevant components, the maximum transmission torque can be easily set within a certain range. Suitable for shafting transmission situations that require safe torque operation to protect important machine components from excessive damage.View More -
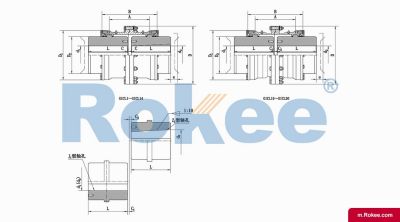
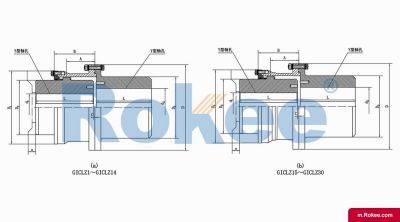
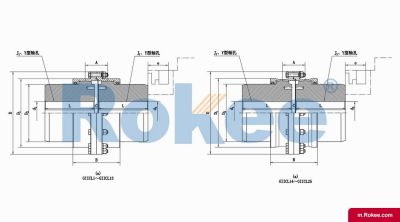
GICL Wide Type Drum Gear Coupling
GICL Drum Gear Coupling has larger inner teeth width, which can transfer torque while compensating for larger axial displacement.View More -
GICLZ Drum Gear Coupling With Intermediate Shaft
Half of the GICLZ Drum Gear Coupling adopts a non-toothed semi-coupling sleeve structure, which is usually connected in pairs or used in occasions with small angular displacement.View More -
GIICL Narrow Type Drum Gear Coupling
GIICL Drum Gear Coupling has small inner teeth width, which can transfer torque while compensating for small axial displacement. Also, its structure is compact and the moment of inertia is low.View More -
GIICLZ Drum Gear Coupling With Intermediate Shaft
Half of the GIICLZ Drum Gear Coupling adopts a non-toothed semi-coupling sleeve structure, which is usually connected in pairs or used in occasions with small angular displacement. Also, its structure is compact and the moment of inertia is low.View More -
GCLD Drum Gear Coupling For Motor
GCLD Drum Gear Coupling is generally used for direct connection with the motor, so it generally has a higher speed and compact structure.View More -
NGCL Drum Gear Coupling With Brake Wheel
NGCL Drum Gear Coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required.View More -
NGCLZ Drum Gear Coupling With Brake Wheel
NGCLZ Drum Gear Coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required. Half of its structure adopts a semi-coupling sleeve design, with smaller angular displacement compensation but more stable braking.View More -
WG Drum Gear Coupling
The overall characteristics of WG Drum Gear Coupling are similar to those of other drum gear couplings, but with a larger modulus design, which can generally transmit greater torque.View More -
WGZ Drum Gear Coupling With Brake Wheel
WGZ Drum Gear Coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for shoe type braking.View More -
WGP Drum Gear Coupling With Brake Discs
WGP Drum Gear Coupling is designed with a brake disc, suitable for disc type braking.View More -
WGT Drum Gear Coupling With Indirect Tube
WGT Drum Gear Coupling is designed with indirect tube, suitable for long distance torque transfer.View More -
WGC Vertical Installation Drum Gear Coupling
WGC Drum Gear Coupling is specially designed for situations where vertical transmission is required, suitable for some vertical transmission systems.View More -
WGJ Drum Gear Coupling With Intermediate Shaft
WGJ Drum Gear Coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance torque transmission, and some are equipped with axial buffers.View More
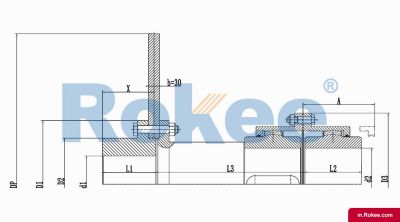
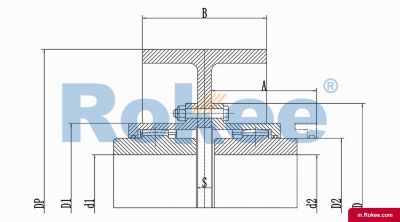
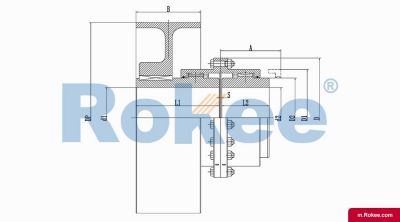
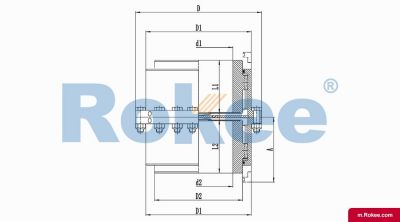
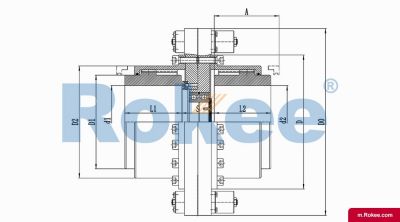
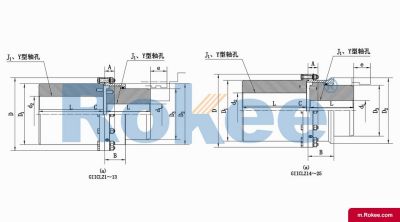
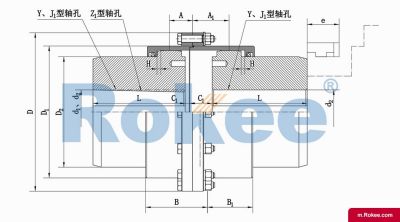
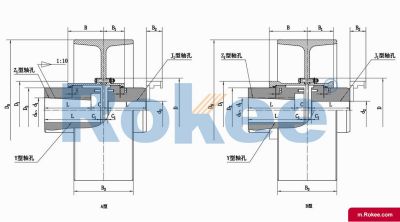
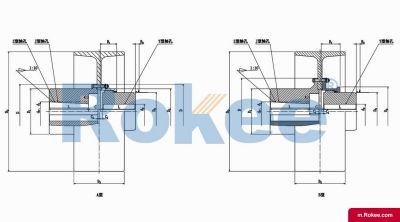
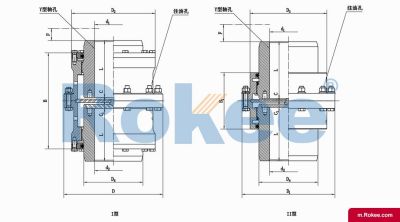
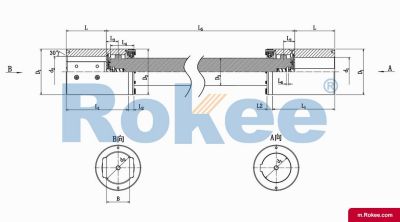
The Curved-tooth Gear Coupling is mainly composed of an inner gear ring, an outer gear shaft sleeve, an end cover, a sealing device, and other parts. Its core lies in the fact that the tooth tips of the outer gear shaft sleeve are made into a drum shape, and the tooth surface is in a circular arc shape, which distinguishes it from other gear couplings. The inner gear ring meshes with the outer gear shaft sleeve, transmitting torque through the contact of the tooth surface. The end cap is used to fix and protect internal components, while the sealing device can effectively prevent dust, impurities, etc. from entering the interior of the coupling, ensuring its normal operation.
The working principle of the Curved-tooth Gear Coupling is relatively simple. During operation, the torque of the driving shaft is transmitted to the inner gear ring through the outer gear shaft sleeve, which in turn drives the driven shaft to rotate. Due to the presence of drum shaped teeth, when there is relative displacement between the two shafts, the contact point between the tooth surface of the drum shaped teeth and the tooth surface of the inner ring gear will change, which enables the coupling to adapt to displacement compensation at certain angles, radial and axial directions. This displacement compensation capability enables the Curved-tooth Gear Coupling to maintain stable transmission performance under complex working conditions.
Performance characteristics
High torque transmission capability: The tooth profile design of the Curved-tooth Gear Coupling is reasonable, with a large contact area on the tooth surface, which can withstand large torque and is particularly suitable for heavy-duty transmission applications.
Good displacement compensation capability: Curved-tooth Gear Couplings can effectively compensate for angular displacement, radial displacement, and axial displacement between two shafts, reduce additional loads caused by misalignment of the shaft system, and improve equipment reliability and service life.
Smooth operation and low noise: The meshing process of the drum shaped teeth is relatively smooth, and compared to other couplings, the noise generated during operation is lower, making it suitable for work environments with strict noise requirements.
Easy installation and maintenance: The structure of the Curved-tooth Gear Coupling is relatively simple, and the alignment requirements for the two shafts during installation are not as strict as those for rigid couplings. In terms of maintenance, the sealing device is easy to replace, and the maintenance of internal components is also relatively convenient.
Curved-tooth Gear Couplings have been widely used in various industrial fields due to their unique structure and excellent performance
Metallurgical industry: In large equipment such as rolling mills and blast furnaces, Curved-tooth Gear Couplings are used to connect motors and reducers, reducers and working machines, etc., to meet their heavy-duty and high impact working conditions.
Mining machinery, such as crushers, ball mills, and other equipment, work in harsh environments and are prone to shaft displacement. The Curved-tooth Gear Coupling, with its excellent displacement compensation capability and high reliability, ensures the stable operation of the equipment.
Petrochemical industry: Curved-tooth Gear Couplings are used to transmit power in equipment such as pumps and compressors. Their corrosion resistance and stable transmission performance ensure the continuity and safety of chemical production.
Power industry: Curved-tooth Gear Couplings have also been widely used in equipment such as steam turbine generators and fans, providing reliable power transmission for power production.
The manufacturing process of Curved-tooth Gear Couplings includes two methods: machining and enveloping machining. In terms of lubrication, some models are equipped with forced thin oil lubrication systems or segmented grease lubrication structures to reduce tooth wear and extend service life. For high-speed Curved-tooth Gear Couplings, lubricating oil is usually used for lubrication, and the smooth discharge of lubricating oil is ensured to avoid the temperature rise of the tooth surface and the accumulation of moisture and dirt.
In the complex and precise field of mechanical power transmission, couplings serve as critical components that bridge driving and driven shafts, ensuring the efficient transfer of torque while accommodating inevitable misalignments. Among the diverse range of couplings available, the curved-tooth gear coupling stands out as a sophisticated and high-performance solution, widely utilized in various industrial applications where reliability, load-bearing capacity, and operational stability are paramount. Unlike conventional straight-tooth counterparts, the curved-tooth design incorporates unique geometric and structural features that address many of the limitations associated with traditional gear couplings, making it a preferred choice for demanding working conditions.
The basic structure of a curved-tooth gear coupling typically consists of several key components, each designed to work in harmony to achieve optimal transmission performance. At the core of the coupling are two geared hubs, which are connected to the driving and driven shafts respectively. These hubs feature curved teeth that are meticulously machined to form a spherical profile, with the center of the sphere aligned precisely on the gear axis. This spherical tooth design is a defining feature of the curved-tooth gear coupling, as it enables the coupling to accommodate various types of misalignments, including angular, radial, and axial displacements. Complementing the geared hubs is a coupling sleeve or an inner gear ring that meshes with the curved teeth of the hubs. In some designs, the sleeve may be constructed from a combination of materials, such as a nylon or polyamide inner layer paired with steel outer components, while all-steel configurations are also common for heavy-duty applications. Additionally, the coupling assembly includes sealing elements, such as oil seals or O-rings, and fastening components like bolts and keys to ensure secure connection and prevent lubricant leakage. The sealing system plays a crucial role in protecting the internal gear meshing from contamination by dust, debris, and moisture, which can significantly impact the service life of the coupling.
The working principle of the curved-tooth gear coupling revolves around the meshing of the curved teeth on the hubs with the corresponding teeth on the sleeve or inner gear ring, enabling the efficient transmission of torque while compensating for shaft misalignments. When the driving shaft rotates, it imparts rotational motion to the connected geared hub, which in turn transfers this motion to the sleeve through the meshing curved teeth. The sleeve then transmits the torque to the second geared hub, which drives the driven shaft. The key advantage of the curved tooth design lies in its ability to distribute the contact stress evenly across the tooth surface during operation. Unlike straight-tooth couplings, where misalignments can lead to concentrated edge loading on the teeth, the curved profile of the teeth in curved-tooth gear couplings ensures that the contact area remains uniform even when the shafts are not perfectly aligned. This even stress distribution not only reduces wear and tear on the tooth surfaces but also allows the coupling to handle higher torque loads. Furthermore, the spherical geometry of the outer teeth enables the hubs to pivot relative to the sleeve, accommodating angular displacements of up to 1.5 degrees in some configurations, which is significantly higher than the 1-degree limit typically found in straight-tooth couplings. This enhanced misalignment compensation capability makes the curved-tooth gear coupling particularly suitable for applications where shaft alignment is challenging, such as in large industrial machinery where thermal expansion and contraction or structural deflection can cause dynamic shifts in shaft positions.
Material selection is a critical factor in determining the performance, durability, and application range of curved-tooth gear couplings. The choice of materials depends on various factors, including the operating conditions (such as temperature, load, and environment), torque requirements, and desired service life. For the geared hubs and sleeves in heavy-duty applications, high-strength alloy steels are commonly used due to their excellent mechanical properties, including high tensile strength, wear resistance, and fatigue resistance. Common alloy steel grades include 45# steel, 40CrMo, and stainless steel, which offer superior performance compared to cast iron or carbon steel. Forged steel is often preferred over cast steel for critical components because the forging process eliminates internal defects such as porosity and inclusions, resulting in a more homogeneous material structure with enhanced mechanical strength. In applications where weight reduction is a consideration, such as in some aerospace or automotive systems, aluminum alloys may be used for non-critical components, although their use is limited to lower torque applications. For the sleeve in maintenance-free designs, polyamide (nylon) or other engineering plastics are frequently employed. These materials offer several advantages, including low friction coefficients, self-lubricating properties, chemical resistance, and the ability to dampen vibration and reduce noise. The combination of steel hubs and polyamide sleeves creates a lightweight, maintenance-free coupling that is suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, from light to moderate torque requirements.
The manufacturing process of curved-tooth gear couplings involves several precision machining operations to ensure the accuracy of the tooth profile and the overall dimensional stability of the components. The process typically begins with the selection and preparation of the raw materials, which may involve forging or casting to form the basic shape of the hubs and sleeves. For forged components, the raw steel is heated to a high temperature and then shaped using a forging press to achieve the desired geometry. This forging process refines the grain structure of the steel, improving its mechanical properties. After forging or casting, the components undergo rough machining operations, such as turning and milling, to remove excess material and achieve approximate dimensions. The next step is the precision machining of the curved teeth, which is a critical operation requiring advanced machining equipment such as CNC gear hobbing machines, gear shaping machines, or wire-cut electrical discharge machining (EDM) tools. The curved tooth profile must be machined with high accuracy to ensure proper meshing and optimal performance. For some high-precision applications, grinding operations are performed on the tooth surfaces to achieve a smooth finish and precise dimensional tolerance, reducing friction and wear during operation. Heat treatment processes, such as quenching and tempering, are also essential to enhance the hardness and wear resistance of the gear teeth. The quenching process involves heating the components to a high temperature and then rapidly cooling them in a quenching medium, while tempering is performed to reduce internal stresses and improve the toughness of the material. Finally, the components are assembled, with the sealing elements and fastening parts installed, and the coupling undergoes rigorous quality inspection to ensure that all dimensions and performance parameters meet the required specifications.
Curved-tooth gear couplings offer a multitude of performance advantages over other types of couplings, making them a versatile and reliable choice for various industrial applications. One of the most significant advantages is their high load-bearing capacity. Due to the even stress distribution across the curved tooth surfaces, these couplings can transmit significantly higher torques compared to straight-tooth couplings of the same size. On average, the load-bearing capacity of curved-tooth gear couplings is 15-20% higher than that of straight-tooth couplings with similar outer diameters. This enhanced torque-carrying capability makes them ideal for heavy-duty applications such as metallurgy, mining, and heavy machinery. Another key advantage is their superior misalignment compensation. As mentioned earlier, curved-tooth gear couplings can accommodate larger angular, radial, and axial displacements, which reduces the need for precise shaft alignment during installation and minimizes the impact of dynamic misalignments during operation. This not only simplifies the installation process but also reduces the wear on other components in the transmission system, such as bearings and shafts. Additionally, the curved tooth design results in smoother operation and lower noise levels. The even meshing of the curved teeth reduces vibration and shock loads, creating a quieter working environment compared to straight-tooth couplings, where edge loading can cause significant noise and vibration. Curved-tooth gear couplings also exhibit high transmission efficiency, typically exceeding 99%, which minimizes energy loss and improves the overall efficiency of the mechanical system. For all-steel configurations, proper lubrication ensures almost wear-free operation, extending the service life of the coupling. In contrast, maintenance-free designs with polyamide sleeves eliminate the need for regular lubrication, reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
The wide range of applications of curved-tooth gear couplings reflects their versatility and adaptability to different operating conditions. They are extensively used in heavy industries such as ferrous metallurgy, where they are employed in rolling mills, continuous casting machines, and other equipment that requires the transmission of high torques under harsh conditions. In the mining industry, curved-tooth gear couplings are used in conveyor systems, crushers, and grinding mills, where they must withstand heavy loads and significant misalignments. The energy sector also relies heavily on these couplings, with applications in gas turbines, wind turbines, and nuclear power plants, where reliability and precision are critical. In the transportation industry, they are used in railway locomotives, marine propulsion systems, and heavy-duty vehicles to transmit power from the engine to the wheels or propellers. Additionally, curved-tooth gear couplings find applications in general machinery such as pumps, compressors, and electric motors, where they ensure efficient torque transmission and compensate for minor misalignments. The ability to adapt to both horizontal and vertical installation orientations further expands their application range, making them suitable for a wide variety of mechanical systems.
Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the long-term performance and reliability of curved-tooth gear couplings. The maintenance requirements vary depending on the type of coupling configuration, with all-steel lubricated couplings requiring more regular maintenance compared to maintenance-free polyamide sleeve designs. For lubricated couplings, regular inspection and replacement of lubricant are critical to prevent wear and corrosion. The lubricant serves to reduce friction between the meshing teeth, dissipate heat, and protect the components from rust and contamination. The frequency of lubrication depends on the operating conditions, with high-load, high-temperature, or dusty environments requiring more frequent lubricant changes. It is also important to inspect the sealing elements regularly to ensure that they are intact and functioning properly, as damaged seals can lead to lubricant leakage and contamination of the gear meshing. For maintenance-free couplings with polyamide sleeves, the primary maintenance task is regular visual inspection to check for signs of wear, cracking, or deformation of the sleeve. If any damage is detected, the sleeve should be replaced promptly to prevent failure of the coupling. Additionally, regular alignment checks should be performed to ensure that the shafts remain within the allowable misalignment limits. Misalignment beyond the recommended range can lead to increased wear, reduced performance, and premature failure of the coupling. Proper installation is also a key aspect of maintenance, as incorrect installation can cause excessive stress on the coupling components and shorten their service life.
In conclusion, the curved-tooth gear coupling is a highly advanced and reliable component in mechanical power transmission systems, offering superior performance characteristics compared to traditional straight-tooth couplings. Its unique curved tooth design enables efficient torque transmission, enhanced misalignment compensation, even stress distribution, and reduced wear, making it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. The careful selection of materials, precision manufacturing processes, and proper maintenance practices are essential to maximizing the performance and service life of these couplings. As industrial machinery continues to evolve towards higher power, higher speed, and more demanding operating conditions, the curved-tooth gear coupling is expected to play an increasingly important role in ensuring the reliability and efficiency of power transmission systems. Its versatility, durability, and performance advantages make it a preferred choice for engineers and manufacturers seeking to optimize the performance of their mechanical systems, from heavy-duty industrial machinery to precision equipment in various sectors.
« Curved-tooth Gear Couplings » Update Date: 2026/1/10
URL: https://m.rokee.com/tags/curved-tooth-gear-couplings.html