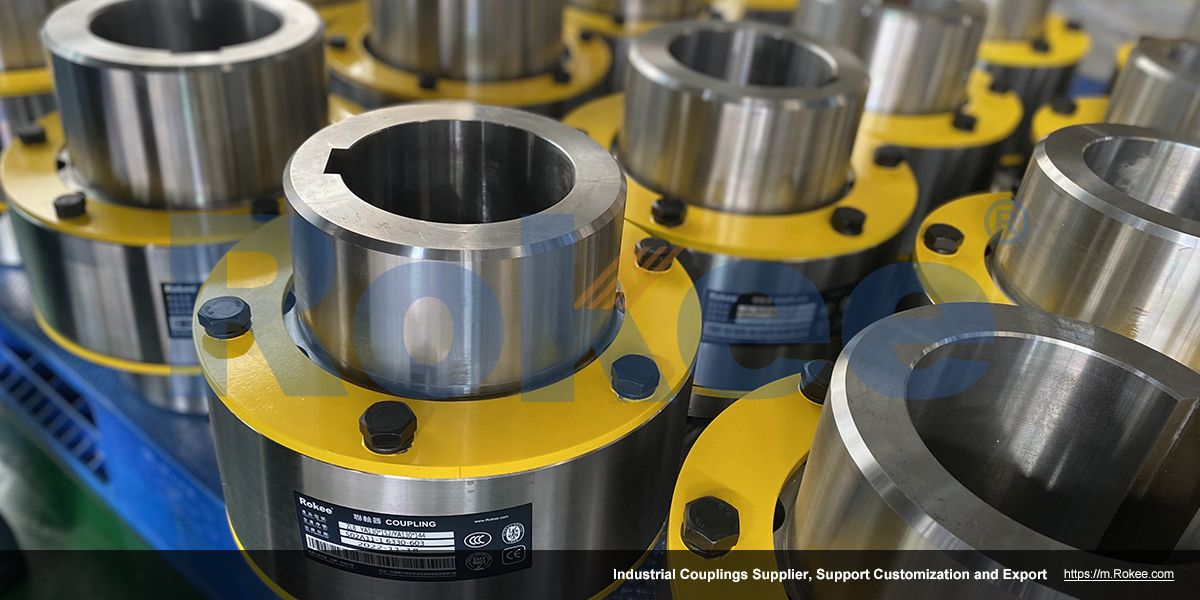
Rokee is a chinese Pin Couplings Manufacturer, provide Pin Couplings processing and customization services, Over the years, with excellent quality, we have been continuously providing many coupling products of various categories and uses complying with multiple standards and a full range of services, from the Pin Couplings selection to final installation and operation, for the industry fields of ferrous metallurgy, nuclear power, gas turbine, wind power, ropeway construction, lifting transportation, general equipment, etc. We strictly comply with quality system requirements and implement the whole process control to become a reliable and trustworthy partner of customers.
Providing customers with better Pin Couplings is always our driving force. Our aim is to transmit power for you and generate value for both of us. We look forward to joining you and becoming your partner for common progress.
-
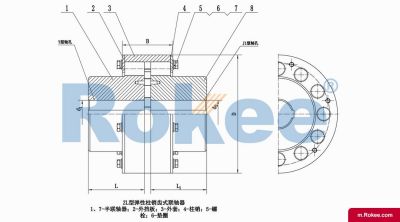
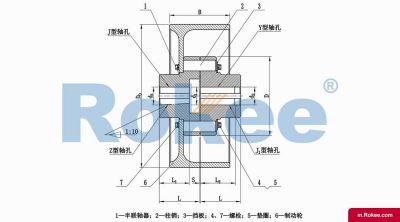
LZ/ZL Elastic Pin Gear Coupling
LZ Pin Gear Coupling is the basic form of this series of couplings.View More -
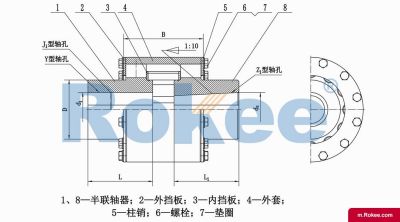
LZD/ZLD Elastic Pin Gear Coupling With Conical Shaft Hole
One end of the LZD Pin Gear Coupling is designed with a conical shaft hole, and the clearance between the semi-couplings is increased to facilitate the fixing space at the shaft end.View More -
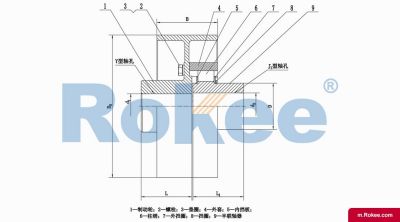
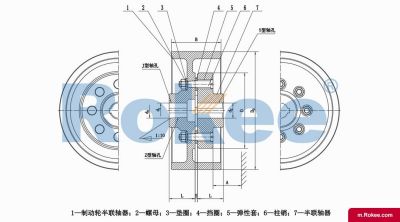
LZZ/ZLL Elastic Pin Gear Coupling With Brake Wheel
LZZ Pin Gear Coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required.View More -
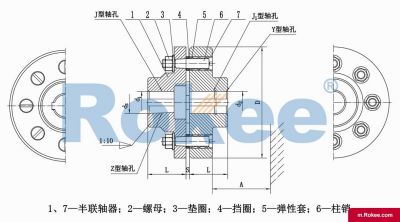
LX/HL Flexible Pin Coupling
LX(HL) Flexible Pin Coupling is the basic form of this series of couplings.View More -
LXZ/HLL Flexible Pin Coupling With Brake Wheel
LXZ(HLL) Flexible Pin Coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required.View More -
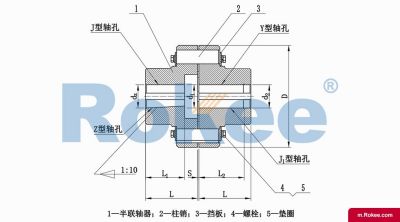
LT/TL Elastic Sleeve Pin Coupling
LT Elastic Sleeve Pin Coupling is the basic form of this series of couplings.View More -
LTZ/TLL Elastic Sleeve Pin Coupling With Brake Wheel
LTZ Elastic Sleeve Pin Coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required.View More
Pin coupling is a type of coupling that uses column pins to connect two halves of the coupling together. According to the different materials of the column pins, Pin couplings can be divided into various types, such as elastic sleeve Pin couplings, cylindrical pin couplings, and elastic Pin couplings. The working principle of the Pin coupling mainly relies on the shear and compression deformation of the column pin to transmit torque, and has a certain ability to compensate for the relative displacement of the two shafts. When the two halves of the coupling undergo relative displacement, the column pin will be subjected to shear and compression, thereby absorbing and compensating for this displacement. Meanwhile, the elastic sleeve or elastic element can also serve as a buffer and shock absorber.
The Pin coupling has a simple and compact structure, making it easy to manufacture and install. Has the ability to compensate for relative offset between two axes, including radial, axial, and angular offsets. Elastic sleeves or components can absorb vibrations and impacts, reducing noise. Suitable for medium and small power shaft transmission, especially for occasions where vibration reduction requirements are not high.
Pin couplings are widely used in various mechanical processing and industrial engineering fields, such as machine tools, pumps, fans, compressors, and other equipment. It is particularly suitable for small and medium power shaft transmission systems with good base rigidity, high centering accuracy, low impact load, and low vibration reduction requirements.
Pin coupling is a mechanical transmission component with a simple structure, easy manufacturing and installation, and has a wide range of application fields and important practical value. When selecting and using, it is necessary to fully consider its characteristics and application requirements to ensure that it can work properly and perform at its best.
In the realm of mechanical power transmission, couplings serve as indispensable components that connect two rotating shafts to transmit torque while accommodating inevitable misalignments and mitigating operational stresses. Among the diverse array of coupling types available, the pin coupling stands out for its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and versatile performance across various industrial scenarios. Characterized by a straightforward design that typically consists of two hubs and a series of pins (often with flexible elements), pin couplings strike a balance between torque transmission efficiency and adaptability to dynamic operating conditions.
At its core, the pin coupling is engineered to address the fundamental challenge of transferring rotational power between two shafts that may not be perfectly aligned. The basic structure of a pin coupling revolves around two primary components: the hubs and the pins. Each hub is designed to attach securely to the end of a respective shaft, usually through keyways or set screws that ensure a tight, non-slip connection during rotation. The hubs are typically flanged, featuring a series of evenly spaced holes around their circumference. These holes are precisely machined to accommodate the pins, which serve as the critical torque-transmitting elements. In many configurations, the pins are paired with bushings or sleeves made from flexible materials, which enhance the coupling's ability to absorb shocks, dampen vibrations, and compensate for misalignments. The simplicity of this design not only facilitates easy manufacturing but also ensures straightforward installation and maintenance, making pin couplings a preferred choice for many industrial applications where operational efficiency and low downtime are paramount.
The working principle of a pin coupling is both elegant and effective. When torque is applied to one of the shafts, it is transferred to the corresponding hub. The pins, which are inserted into the holes of this hub, then transmit the torque to the second hub by virtue of their mechanical engagement. As the first hub rotates, the pins exert a force on the inner walls of the holes in the second hub, causing it to rotate in unison. This torque transmission occurs with minimal energy loss, provided the coupling is properly sized and maintained. A key aspect of the pin coupling's functionality lies in its ability to accommodate different types of misalignments, including angular, radial, and axial misalignments. Angular misalignment occurs when the shafts are not collinear but intersect at a small angle, while radial misalignment refers to a parallel offset between the shafts. Axial misalignment, on the other hand, involves a linear displacement along the axis of the shafts. The flexible elements (such as bushings or elastic pins) in the coupling allow for slight movements between the hubs, absorbing the stresses that would otherwise be transferred to the shafts and other connected components. This flexibility also contributes to vibration damping, reducing noise and minimizing wear on the machinery, thereby extending the overall service life of the system.
Pin couplings are available in several distinct configurations, each tailored to specific operational requirements and load conditions. One of the most common types is the elastic pin coupling, which utilizes pins made from non-metallic elastic materials such as nylon or polyurethane. These elastic pins are placed directly into the flange holes of the two hubs, eliminating the need for additional bushings. The elastic nature of the pins allows for effective shock absorption and misalignment compensation, while also providing the advantage of self-lubrication. This self-lubricating property not only saves on lubrication costs but also ensures a clean working environment, as there is no risk of lubricant leakage. Elastic pin couplings are particularly well-suited for low to medium speed and torque applications, where their simple structure and low maintenance requirements offer significant benefits.
Another prevalent configuration is the pin bush coupling, which features metal pins paired with elastomeric bushes. The bushes are inserted into the holes of the hubs, and the metal pins pass through these bushes to connect the two hubs. This design combines the high torque capacity of metal pins with the flexibility and vibration-damping properties of elastomeric bushes. The bushes act as sacrificial wear components, protecting the more expensive hubs and pins from premature damage. When the bushes wear out, they can be easily replaced without disassembling the entire coupling or moving the connected shafts, simplifying maintenance and reducing downtime. Pin bush couplings are capable of handling higher torque loads compared to elastic pin couplings, making them suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications such as pumps, compressors, and conveyors.
Additional variations of pin couplings include spiral pin couplings, cross-block couplings, and ring couplings. Spiral pin couplings feature a helical arrangement of elastomeric pins, which enhances their flexibility and energy absorption capabilities under dynamic loads. This design ensures even load distribution across the pins, making them ideal for applications with frequent start-stop cycles. Cross-block couplings utilize a cross-shaped elastomeric insert that excels at correcting angular and parallel misalignments, offering high torsional stiffness and reliable performance in continuous operation. Ring couplings, on the other hand, use a continuous ring-shaped elastomeric element between flanged hubs, providing a compact and lightweight solution that effectively reduces noise and vibration. These specialized configurations expand the range of applications for pin couplings, allowing them to meet the unique demands of different industrial sectors.
Material selection plays a crucial role in determining the performance, durability, and suitability of a pin coupling for specific applications. The hubs of pin couplings are typically manufactured from metallic materials that offer high strength and rigidity. Common choices include cast iron, cast steel, and forged steel. Cast iron is often used for light to medium load applications due to its cost-effectiveness and good machinability. Cast steel, with its higher tensile strength and impact resistance, is preferred for heavy-duty applications where the coupling is subjected to high torque loads and harsh operating conditions. Forged steel, which offers superior mechanical properties compared to cast steel, is used in critical applications where reliability and durability are of utmost importance. The selection of hub material is also influenced by environmental factors, such as exposure to corrosion, high temperatures, or chemical substances, which may require the use of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant alloys.
The pins and bushings (if used) are made from materials that balance strength and flexibility. Metal pins are commonly crafted from high-carbon steel or alloy steel, which provide the necessary tensile strength and wear resistance to transmit high torques. Elastic pins, on the other hand, are made from non-metallic materials such as nylon (particularly MC nylon) or polyurethane. These materials offer excellent flexibility, self-lubrication, and shock absorption properties. Nylon pins are widely used due to their low cost, good chemical resistance, and ability to operate within a temperature range of -20°C to 80°C. Polyurethane pins, while more expensive, offer superior abrasion resistance and a wider temperature tolerance, making them suitable for more demanding applications. Elastomeric bushings are typically made from rubber or polyurethane, chosen for their ability to absorb vibrations and compensate for misalignments without compromising torque transmission efficiency.
The versatility of pin couplings is reflected in their wide range of applications across various industrial sectors. In industrial machinery, pin couplings are commonly used to connect motors to pumps, compressors, generators, and conveyor systems. Their ability to transmit torque efficiently while dampening vibrations makes them ideal for these applications, where smooth operation and reliability are essential. In the automotive industry, pin couplings are utilized to connect the engine shaft to the transmission shaft, helping to reduce shock loads and vibrations during acceleration and deceleration. The marine industry also relies on pin couplings for connecting engine shafts to propeller shafts, where their corrosion resistance and ability to handle high torque loads are critical for reliable propulsion.
Pin couplings are also finding applications in specialized fields such as aerospace, where they are used in aircraft engines to connect the engine shaft to the generator shaft. In this context, their lightweight design, high reliability, and low maintenance requirements are highly valued. Clinical laboratory equipment, such as shakers, also benefits from the use of pin couplings. These applications require precise torque transmission and minimal vibration to protect delicate samples and ensure accurate test results, which pin couplings are well-equipped to provide. Even in emerging areas such as bicycle sharing station mechanisms, pin couplings are used due to their compact size, low maintenance needs, and ability to operate reliably in outdoor environments.
Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the long-term performance and reliability of pin couplings. Fortunately, their simple design makes maintenance relatively straightforward. Regular inspection is the cornerstone of effective maintenance, involving checks for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. The pins and bushings should be inspected periodically for wear, cracking, or deformation, as these are the components most prone to damage. If excessive wear is detected, the pins or bushings should be replaced promptly to prevent further damage to the hubs or shafts. In the case of elastic pin couplings, replacing the pins is a simple process that involves removing the retaining plates (if present) and inserting new pins, without the need to disassemble the entire coupling.
Lubrication is another important maintenance consideration, although it varies depending on the type of pin coupling. Elastic pin couplings with non-metallic pins are self-lubricating and do not require additional lubrication, which simplifies maintenance and reduces operational costs. However, pin bush couplings with metal pins may require periodic lubrication to reduce friction between the pins and bushings, extending their service life. When lubrication is necessary, it is important to use the appropriate type and amount of lubricant, as specified by the application requirements. Additionally, checking the alignment of the shafts is crucial, as excessive misalignment can lead to premature wear of the coupling components and increased stress on the connected machinery. Shaft alignment should be checked during installation and periodically thereafter, particularly after any maintenance or repair work.
Despite their numerous advantages, pin couplings also have certain limitations that must be considered when selecting a coupling for a specific application. One of the primary limitations is their lower precision compared to other types of couplings, such as rigid couplings or disc couplings. This makes them unsuitable for high-precision applications where exact shaft alignment is required, such as in some machine tool operations. Pin couplings also have limited capacity to handle large axial loads or bending moments, which can cause premature failure if not properly accounted for. Another limitation is that some configurations may generate noise during operation, particularly at high speeds, which can be a concern in noise-sensitive environments.
Furthermore, the elastic elements in pin couplings (such as nylon pins or rubber bushings) are susceptible to degradation over time, especially when exposed to extreme temperatures, chemicals, or ultraviolet radiation. This degradation can reduce the coupling's flexibility and shock absorption capabilities, requiring more frequent replacement of components. It is also important to note that pin couplings are not suitable for applications with very high speeds, as the centrifugal forces generated can place excessive stress on the pins and hubs, leading to premature failure. Understanding these limitations is crucial for selecting the right coupling type and ensuring optimal performance in a given application.
In conclusion, pin couplings represent a vital category of mechanical components that play a critical role in power transmission systems across a wide range of industries. Their simple yet effective design, combined with advantages such as easy installation, low maintenance, good vibration damping, and the ability to accommodate misalignments, makes them a preferred choice for many applications. The diverse configurations and material options available allow pin couplings to be tailored to meet the specific requirements of different operating conditions, from light-duty industrial machinery to heavy-duty marine propulsion systems. While they have certain limitations, such as lower precision and limited high-speed capability, these can be effectively managed through proper selection, installation, and maintenance.
As industrial technology continues to evolve, pin couplings are likely to remain a key component in power transmission systems, with ongoing improvements in materials and design further enhancing their performance and versatility. Whether in traditional industrial settings or emerging specialized fields, the reliability and cost-effectiveness of pin couplings ensure their continued relevance in the global mechanical engineering landscape. By understanding the fundamental principles, applications, and maintenance requirements of pin couplings, engineers and maintenance professionals can make informed decisions that optimize the performance and longevity of their mechanical systems, ultimately contributing to increased operational efficiency and reduced downtime.
« Pin Couplings » Update Date: 2026/1/10
URL: https://m.rokee.com/tags/pin-couplings.html