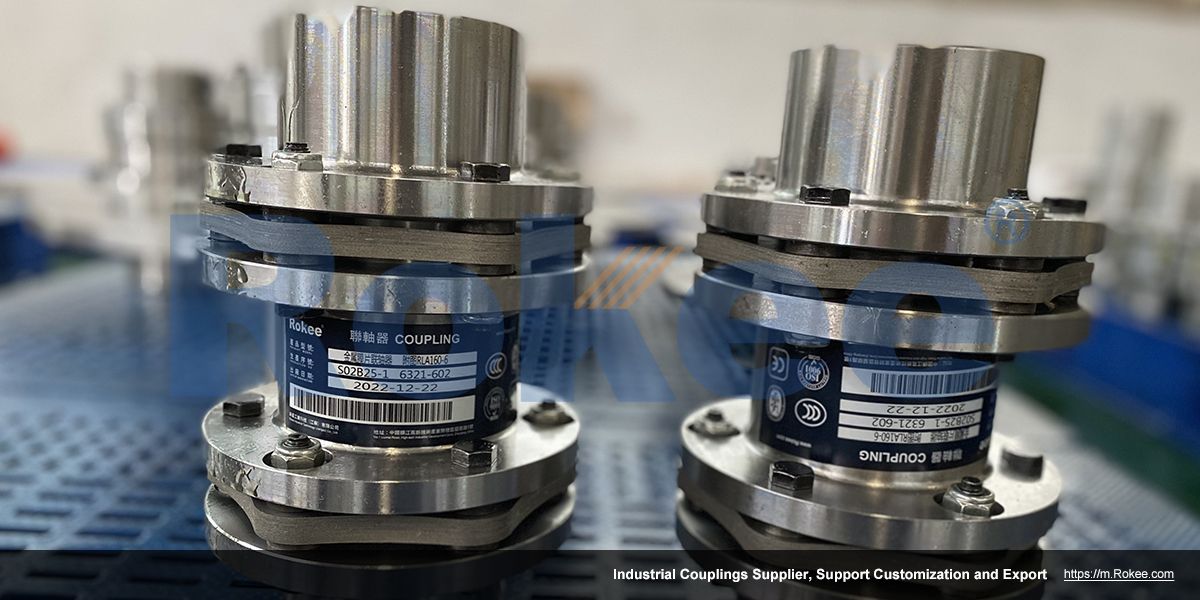
Rokee is a chinese Flexible Membrane Couplings Manufacturer, provide Flexible Membrane Couplings processing and customization services, Over the years, with excellent quality, we have been continuously providing many coupling products of various categories and uses complying with multiple standards and a full range of services, from the Flexible Membrane Couplings selection to final installation and operation, for the industry fields of ferrous metallurgy, nuclear power, gas turbine, wind power, ropeway construction, lifting transportation, general equipment, etc. We strictly comply with quality system requirements and implement the whole process control to become a reliable and trustworthy partner of customers.
Providing customers with better Flexible Membrane Couplings is always our driving force. Our aim is to transmit power for you and generate value for both of us. We look forward to joining you and becoming your partner for common progress.
-
RLM Standard Single Section Small Metal Diaphragm Coupling
The RLM standard single section small metal diaphragm coupling is suitable for various industrial process pumps and small torque working situations with a working speed not exceeding 5000rpm, and cannot compensate for radial errors.View More -
RLMD Standard Double Section Small Metal Diaphragm Coupling
The RLMD standard double section small metal diaphragm coupling is suitable for various industrial process pumps and small torque working occasions with a working speed not exceeding 5000rpm.View More -
RLA Standard Single Section Metal Diaphragm Coupling
The classic design of metal flexible diaphragm couplings,reliable choice for medium to low speed applications,but it cannot compensate for radial deviation.View More -
RLAD Standard Double Section Metal Diaphragm Coupling
The classic design of metal flexible diaphragm couplings is a reliable choice for medium to low speed applications.View More -
RLAR Single Shaft Sleeve Reverse-mounting Metal Diaphragm Coupling
Single side shaft sleeve reverse installation design, suitable for occasions with limited shaft head distance.View More -
RLARD Double Shaft Sleeve Reverse-mounting Metal Diaphragm Coupling
The double-sided shaft sleeve reverse installation design is also applicable in situations where the distance from the shaft head is limited or the additional bending moment is smaller.View More -
RLAF Large & Small Shaft Mounted Metal Diaphragm Coupling
The size difference design of the bilateral shaft sleeve is suitable for situations where the diameter difference between the two ends of the shaft is significant.View More -
RLAT Super Long Wheelbase Metal Diaphragm Coupling
Adopting an intermediate shaft design, suitable for ultra long shaft spacing power transmission applications.View More -
RLQA No Flange Quick Installation Metal Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for various industrial process pumps, fans, and other medium to low speed applications, with a maximum speed generally not exceeding 25000 rpm. It meets the requirements of API610/ISO14691 and is one of the first products for API applications.View More -
RLQF Flange Type Quick Installation Metal Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for drum pressure fans, turbine compressors, and other high speed applications, with a maximum speed of up to 35000rpm.View More -
RLQU Improved Flange Quick Installation Metal Diaphragm Coupling
The improved RLQF has smaller additional bending moments and better performance. Suitable for drum pressure fans, turbine compressors, and other high speed applications.View More -
RLHD High Speed Metal Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for higher speed applications, it also adopts a flexible component integrated assembly design, with a maximum speed of up to 42000rpm.View More -
JMI Single Diaphragm Coupling With Counterbore
JMI metal diaphragm coupling adopts the single-piece design, suitable for short distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at one end has a counterbore, facilitating the fixing of the shaft end.View More -
JMIJ Double Diaphragm Coupling With Intermediate Shaft
JMIJ metal diaphragm coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at one end has a counterbore, facilitating the fixing of the shaft end.View More -
JMII Single Diaphragm Coupling Without Counterbore
JMII metal diaphragm coupling also adopts the single-piece design but has no counterbore, suitable for short distance transmission, with more compact structure.View More -
JMIIJ Double Diaphragm Coupling With Intermediate Shaft
JMIIJ Diaphragm Coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at both ends have no counterbore.View More
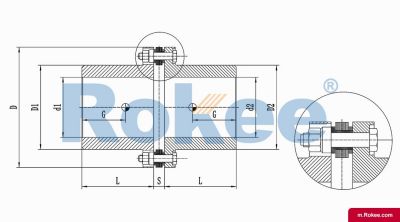
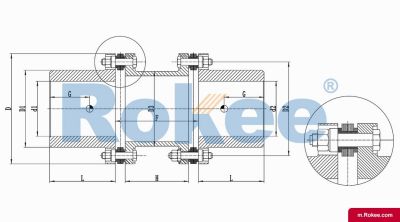
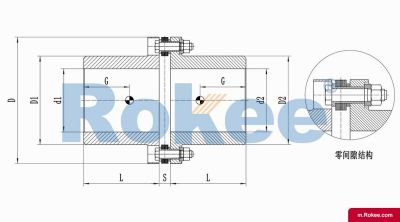
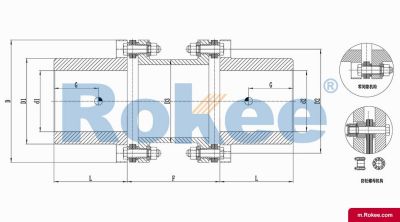
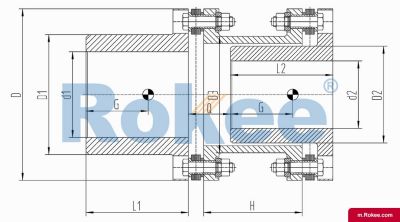
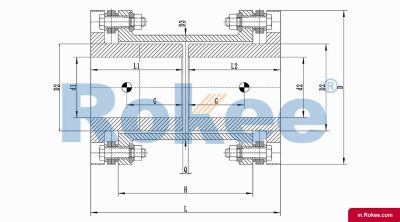
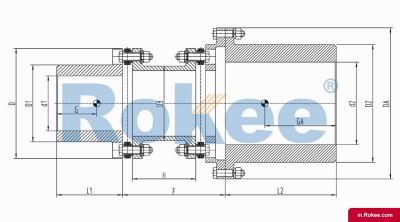
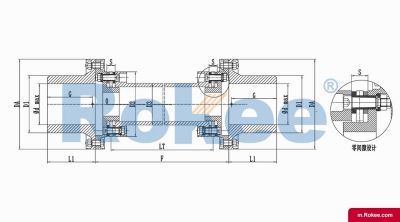
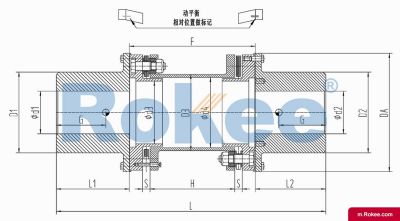
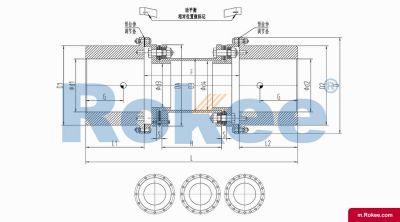
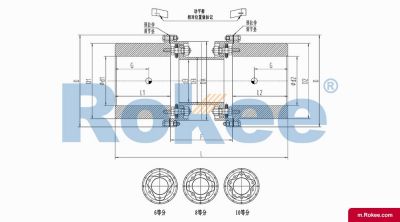
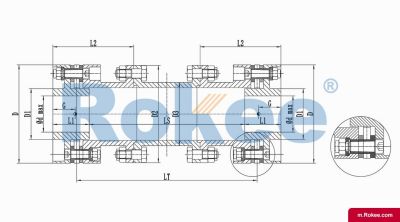
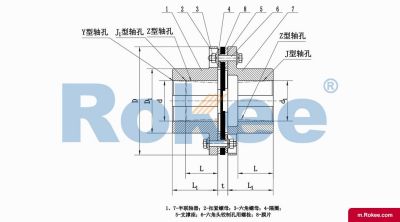
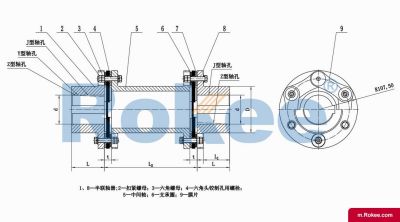
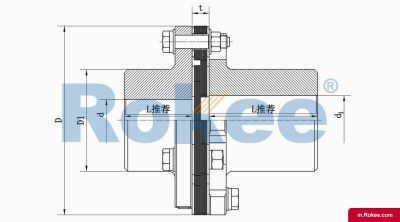
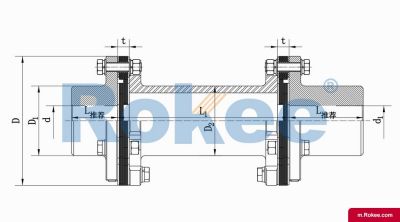
Flexible membrane coupling is a high-performance metal elastic element flexible coupling. The flexible membrane coupling is composed of several sets of stainless steel thin plates connected in a staggered manner to the two halves of the coupling, with each set of membranes consisting of several stacked pieces. This design endows the flexible membrane coupling with unique elasticity and flexibility, enabling it to compensate for the relative displacement between the two shafts. The working principle of flexible membrane couplings mainly relies on the elastic deformation of the diaphragm. When there is relative displacement between the two axes, the diaphragm undergoes elastic deformation to absorb and compensate for this displacement, ensuring smooth and reliable transmission.
Flexible membrane couplings can compensate for axial, radial, and angular offsets between two shafts. Compared with toothed couplings, their angular displacement can be twice as large, and the reaction force is small during radial displacement, resulting in greater flexibility. Due to the elastic deformation of the diaphragm, the flexible membrane coupling has a significant shock absorption effect and does not require lubrication, so it operates without noise or wear. Flexible membrane couplings are suitable for working environments with high temperatures, high speeds, and corrosive media, and can operate stably under harsh conditions. The transmission efficiency can reach 99.86%, especially suitable for medium and high-speed high-power transmission. The flexible membrane coupling has a compact structure, light weight, small volume, and is easy to assemble and disassemble without the need to move the machine.
Flexible membrane couplings are widely used in shaft transmission of various mechanical devices, such as water pumps, fans, compressors, hydraulic machinery, petroleum machinery, printing machinery, textile machinery, chemical machinery, mining machinery, metallurgical machinery, aviation, naval high-speed power transmission systems, steam turbines, piston type power mechanical transmission systems, and generator sets high-speed high-power mechanical transmission systems. According to the number and structure of membranes, flexible membrane couplings can be divided into various types such as single membrane couplings and double membrane couplings. Double membrane couplings are more common in practical applications due to their ability to simultaneously bend in different directions to compensate for eccentricity.
The installation of flexible membrane couplings requires following certain steps and precautions to ensure their normal operation and extend their service life. Before installation, the end faces of both shafts should be cleaned and the fit checked; After installation, all screws should be checked for looseness and repeatedly tightened to ensure they do not loosen. In addition, to prevent micro motion wear of the diaphragm during high-speed operation, solid lubricants such as molybdenum disulfide can be applied between the diaphragms or the diaphragm surface can be treated with anti wear coatings.
In the realm of mechanical power transmission, the need to connect rotating shafts while accommodating misalignments, transmitting torque efficiently, and ensuring long-term reliability has driven the development of various coupling technologies. Among these, the flexible membrane coupling stands out as a high-performance solution, leveraging the elastic deformation of metallic diaphragms to achieve seamless power transfer without the need for lubrication or complex maintenance. Unlike traditional couplings that rely on rubber or plastic elastomers, flexible membrane couplings utilize metal components, granting them superior resistance to high temperatures, corrosion, and mechanical stress. This makes them indispensable in a wide range of industrial, marine, and aerospace applications where precision and durability are paramount. As modern machinery continues to evolve toward higher speeds, greater power densities, and more extreme operating conditions, the role of flexible membrane couplings in ensuring operational stability and efficiency has become increasingly critical.
The fundamental working principle of a flexible membrane coupling revolves around the ability of thin metallic diaphragms to transmit torque while compensating for axial, radial, and angular misalignments between connected shafts. A typical coupling assembly consists of two hubs that attach to the driving and driven shafts, respectively, and one or more sets of diaphragms that connect these hubs. The diaphragms are usually arranged in a stacked configuration, with multiple thin sheets of metal bolted alternately to the hubs. When torque is applied, it is transferred from the driving hub to the outer diameter of the diaphragms, then across the spacer (if present) to the inner diameter of the diaphragms on the driven side, and finally to the driven hub. This transfer of torque occurs through the elastic tension and compression of the diaphragm material, which allows for slight deformations without permanent damage. These deformations are what enable the coupling to accommodate misalignments—angular misalignment is compensated by the bending of the diaphragms, axial displacement by their stretching or compressing, and radial misalignment by a combination of these movements. Importantly, this flexing action occurs without any sliding contact between components, eliminating the need for lubrication and reducing wear significantly.
The structural design of flexible membrane couplings varies to suit different application requirements, but the core components remain consistent: hubs, diaphragms, and connecting bolts. Hubs are typically machined from high-strength metals such as steel or aluminum alloy, designed to provide a secure fit with the shafts through keyways, taper fits, or expansion sleeves. The choice of hub design depends on the shaft diameter, torque requirements, and ease of installation—for example, expansion sleeves are preferred in high-speed applications as they provide a uniform grip without the stress concentrations associated with keyways. Diaphragms, the most critical component, are usually made from stainless steel or other high-performance alloys, with a contour often shaped to approximate a hyperbola. This contoured design ensures uniform shear stress distribution across the diaphragm surface, minimizing bending stresses and reducing the risk of fatigue failure. Some couplings feature single diaphragms for simple applications, while others use multiple convolution diaphragms or stacked diaphragm packs to enhance misalignment compensation capabilities and torque transmission capacity. Spacers, when included, are used to accommodate larger distances between shafts and can be solid or hollow, with hollow spacers offering weight reduction for high-speed operation.
Material selection is a key factor in determining the performance and lifespan of flexible membrane couplings. The diaphragms, being the primary load-bearing and flexing components, require materials with high tensile strength, excellent fatigue resistance, and good corrosion resistance. Stainless steel is the most commonly used material for diaphragms, with grades such as 15-5 PH offering an optimal balance of strength and flexibility. This material is particularly suitable for harsh environments, including those with corrosive media or wide temperature fluctuations. For extreme high-temperature applications, such as in gas turbine systems, nickel-based alloys like Inconel may be used, as they retain their mechanical properties at temperatures exceeding 250°C. Hubs are typically manufactured from carbon steel for general industrial applications, while aluminum alloy is preferred for lightweight, high-speed applications where minimizing rotational inertia is important. The connecting bolts are also critical, with high-strength alloy steel bolts used to ensure a secure connection between the diaphragms and hubs, preventing loosening under dynamic loads. The selection of materials is always tailored to the specific operating conditions, including temperature range, torque requirements, environmental contaminants, and rotational speed.
One of the most notable advantages of flexible membrane couplings is their maintenance-free operation, a direct result of their all-metal construction and lack of sliding parts. Unlike gear couplings, which require regular lubrication to prevent wear and corrosion, or rubber couplings, which degrade over time due to ozone, heat, or chemical exposure, flexible membrane couplings can operate for years without any maintenance other than periodic inspection. This not only reduces operational costs but also minimizes downtime, a crucial factor in industries such as power generation, petrochemical processing, and manufacturing where continuous operation is essential. Additionally, these couplings exhibit high transmission efficiency, typically exceeding 99.8%, as there is no power loss due to sliding friction. Their compact design and light weight make them suitable for applications with limited installation space, while their lack of rotational clearance ensures precise torque transmission, making them ideal for precision machinery such as CNC machine tools and servo systems.
The performance characteristics of flexible membrane couplings make them suitable for a diverse range of applications across multiple industries. In the aerospace sector, they are used to transmit power between gas turbine engines and accessory systems in military and commercial aircraft, where their lightweight, high-reliability, and maintenance-free operation are critical. In marine applications, they are employed in ship propulsion systems, connecting diesel engines or gas turbines to propeller shafts, as they can withstand the corrosive marine environment and compensate for shaft misalignments caused by hull flexing. In industrial settings, they are widely used in pumps, fans, compressors, and rolling mills—for example, in large ethylene plants, they are retrofitted to compressor trains to handle increased torque loads while minimizing downtime. They are also essential in renewable energy systems, such as wind turbines, where they connect the gearbox to the generator, accommodating misalignments caused by wind-induced vibrations and transmitting torque efficiently.
The selection of a flexible membrane coupling for a specific application requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Torque matching is the primary consideration— the rated torque of the coupling must exceed the maximum operating torque of the system, including peak torques during startup or load fluctuations. A safety factor of 1.2 to 1.5 is typically applied for steady-state operations, while higher factors are required for applications with frequent start-stop cycles or shock loads. Rotational speed is another critical parameter, as the coupling must be designed to withstand the centrifugal forces generated at high speeds. The maximum allowable speed is determined by the material strength of the diaphragms and the outer diameter of the coupling—larger diameters limit the maximum speed due to increased centrifugal stress. Misalignment compensation requirements must also be evaluated, with the coupling’s rated compensation capacity exceeding the expected misalignments caused by installation errors, thermal expansion, or shaft deflection. Environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, and corrosive media, dictate the choice of materials—for example, high-temperature applications require heat-resistant alloys, while marine environments demand corrosion-resistant stainless steel.
Despite their high reliability, flexible membrane couplings are not immune to failure, and understanding potential failure modes is essential for ensuring long-term operation. The most common cause of failure is excessive misalignment, which places undue stress on the diaphragms, leading to fatigue cracking over time. To mitigate this, proper installation and alignment are critical—laser alignment tools are recommended to ensure that shaft misalignments are kept within the coupling’s rated limits. Another potential failure mode is bolt loosening, which can occur due to dynamic loads or improper torquing during installation. Using lock washers or thread-locking compounds can help prevent this issue. Material fatigue is also a concern, particularly in applications with high cyclic loads. Regular inspection of the diaphragms for signs of cracking, deformation, or corrosion is essential, with replacement recommended at the first sign of damage. In addition, operating the coupling beyond its rated torque or speed can lead to catastrophic failure, highlighting the importance of proper selection and adherence to operational limits.
Advancements in design and manufacturing technologies have continued to enhance the performance of flexible membrane couplings. Finite element analysis (FEA) has become a standard tool in the design process, allowing engineers to simulate stress distribution, fatigue life, and misalignment compensation capabilities with high precision. This has enabled the optimization of diaphragm contours and thicknesses, resulting in couplings with higher torque capacities and longer service lives. Modern manufacturing processes, such as precision stamping and CNC machining, have improved the accuracy and consistency of diaphragm production, ensuring uniform performance across batches. Additionally, the development of new materials, such as advanced composite alloys, has expanded the operating range of these couplings, allowing them to handle higher temperatures, greater torques, and more corrosive environments than ever before. These technological advancements have made flexible membrane couplings even more versatile and reliable, enabling their use in increasingly demanding applications.
In comparison to other types of flexible couplings, flexible membrane couplings offer several distinct advantages. When compared to gear couplings, they eliminate the need for lubrication, reduce maintenance requirements, and operate with lower noise levels. They also avoid the sliding contact that causes wear in gear couplings, resulting in longer service lives. Compared to rubber or elastomeric couplings, they offer superior temperature and chemical resistance, higher torque transmission capacity, and better precision. Elastomeric couplings are prone to degradation over time, especially in harsh environments, while flexible membrane couplings maintain their performance indefinitely under proper operating conditions. However, it is important to note that flexible membrane couplings have lower torsional flexibility than elastomeric couplings, making them less suitable for applications requiring significant vibration damping. In such cases, a balance must be struck between precision and damping, with some applications using hybrid coupling designs to combine the benefits of both technologies.
The future of flexible membrane couplings is likely to be shaped by the ongoing demand for higher performance, greater efficiency, and improved reliability in mechanical systems. As industries such as aerospace, renewable energy, and advanced manufacturing continue to push the boundaries of speed and power, couplings will need to be designed to handle even more extreme conditions. This may involve the development of new materials with enhanced properties, such as higher strength-to-weight ratios or improved resistance to extreme temperatures. The integration of smart monitoring technologies is another promising area—sensors embedded in the diaphragms or hubs could provide real-time data on stress levels, temperature, and misalignment, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing the risk of unexpected failure. Additionally, the trend toward lightweight and compact designs will drive further optimization of coupling geometries, using advanced simulation tools to minimize weight while maximizing performance.
In conclusion, flexible membrane couplings represent a sophisticated and reliable solution for power transmission in a wide range of applications. Their unique working principle, which leverages the elastic deformation of metallic diaphragms, allows them to transmit torque efficiently while compensating for shaft misalignments, all without the need for lubrication. The careful selection of materials, optimized structural design, and maintenance-free operation make them ideal for harsh and demanding environments, from aerospace and marine propulsion to industrial machinery and renewable energy systems. Proper selection, installation, and regular inspection are essential to ensure their long-term performance, while ongoing advancements in design and manufacturing technologies continue to expand their capabilities. As modern machinery becomes increasingly complex and demanding, flexible membrane couplings will remain a critical component in ensuring operational stability, efficiency, and reliability, playing a vital role in the advancement of industrial and technological progress.
« Flexible Membrane Couplings » Update Date: 2026/1/10
URL: https://m.rokee.com/tags/flexible-membrane-couplings.html