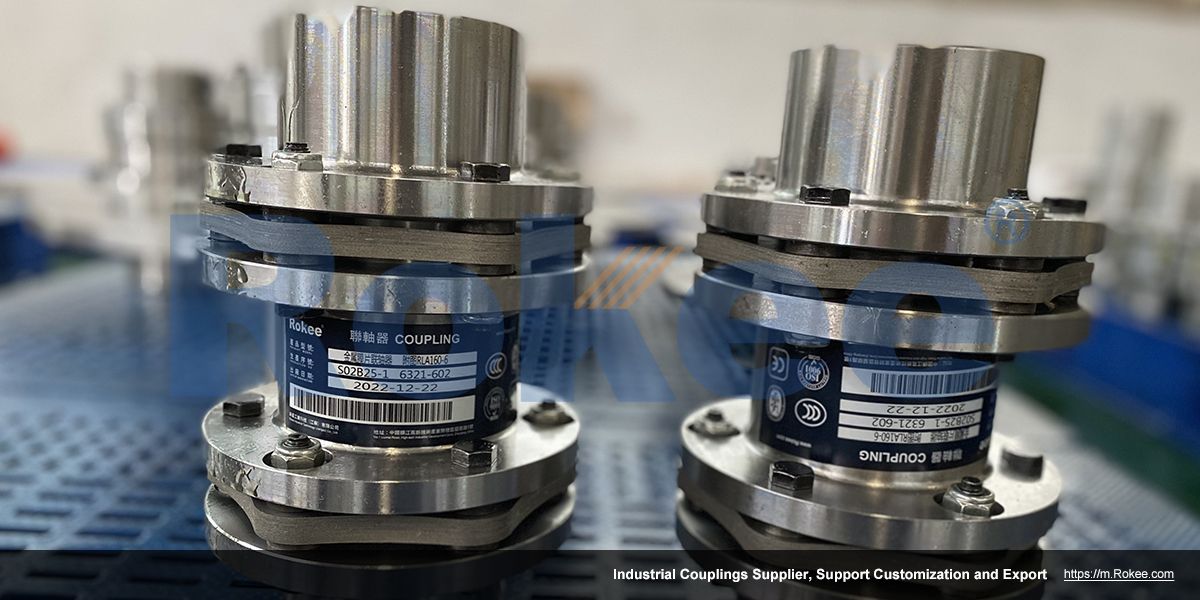
Rokee is a chinese Membrane Couplings Manufacturer, provide Membrane Couplings processing and customization services, Over the years, with excellent quality, we have been continuously providing many coupling products of various categories and uses complying with multiple standards and a full range of services, from the Membrane Couplings selection to final installation and operation, for the industry fields of ferrous metallurgy, nuclear power, gas turbine, wind power, ropeway construction, lifting transportation, general equipment, etc. We strictly comply with quality system requirements and implement the whole process control to become a reliable and trustworthy partner of customers.
Providing customers with better Membrane Couplings is always our driving force. Our aim is to transmit power for you and generate value for both of us. We look forward to joining you and becoming your partner for common progress.
-
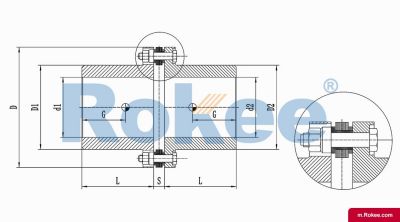
RLM Standard Single Section Small Metal Diaphragm Coupling
The RLM standard single section small metal diaphragm coupling is suitable for various industrial process pumps and small torque working situations with a working speed not exceeding 5000rpm, and cannot compensate for radial errors.View More -
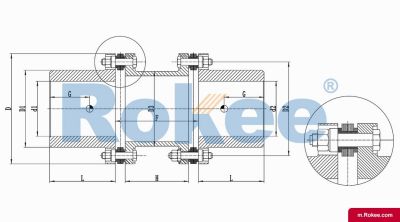
RLMD Standard Double Section Small Metal Diaphragm Coupling
The RLMD standard double section small metal diaphragm coupling is suitable for various industrial process pumps and small torque working occasions with a working speed not exceeding 5000rpm.View More -
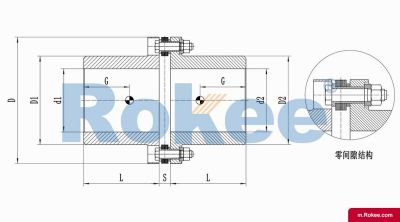
RLA Standard Single Section Metal Diaphragm Coupling
The classic design of metal flexible diaphragm couplings,reliable choice for medium to low speed applications,but it cannot compensate for radial deviation.View More -
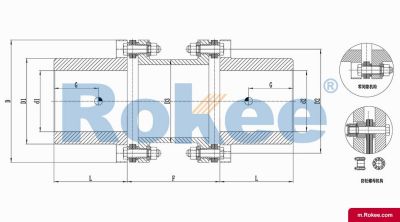
RLAD Standard Double Section Metal Diaphragm Coupling
The classic design of metal flexible diaphragm couplings is a reliable choice for medium to low speed applications.View More -
RLAR Single Shaft Sleeve Reverse-mounting Metal Diaphragm Coupling
Single side shaft sleeve reverse installation design, suitable for occasions with limited shaft head distance.View More -
RLARD Double Shaft Sleeve Reverse-mounting Metal Diaphragm Coupling
The double-sided shaft sleeve reverse installation design is also applicable in situations where the distance from the shaft head is limited or the additional bending moment is smaller.View More -
RLAF Large & Small Shaft Mounted Metal Diaphragm Coupling
The size difference design of the bilateral shaft sleeve is suitable for situations where the diameter difference between the two ends of the shaft is significant.View More -
RLAT Super Long Wheelbase Metal Diaphragm Coupling
Adopting an intermediate shaft design, suitable for ultra long shaft spacing power transmission applications.View More -
RLQA No Flange Quick Installation Metal Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for various industrial process pumps, fans, and other medium to low speed applications, with a maximum speed generally not exceeding 25000 rpm. It meets the requirements of API610/ISO14691 and is one of the first products for API applications.View More -
RLQF Flange Type Quick Installation Metal Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for drum pressure fans, turbine compressors, and other high speed applications, with a maximum speed of up to 35000rpm.View More -
RLQU Improved Flange Quick Installation Metal Diaphragm Coupling
The improved RLQF has smaller additional bending moments and better performance. Suitable for drum pressure fans, turbine compressors, and other high speed applications.View More -
RLHD High Speed Metal Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for higher speed applications, it also adopts a flexible component integrated assembly design, with a maximum speed of up to 42000rpm.View More -
JMI Single Diaphragm Coupling With Counterbore
JMI metal diaphragm coupling adopts the single-piece design, suitable for short distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at one end has a counterbore, facilitating the fixing of the shaft end.View More -
JMIJ Double Diaphragm Coupling With Intermediate Shaft
JMIJ metal diaphragm coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at one end has a counterbore, facilitating the fixing of the shaft end.View More -
JMII Single Diaphragm Coupling Without Counterbore
JMII metal diaphragm coupling also adopts the single-piece design but has no counterbore, suitable for short distance transmission, with more compact structure.View More -
JMIIJ Double Diaphragm Coupling With Intermediate Shaft
JMIIJ Diaphragm Coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at both ends have no counterbore.View More
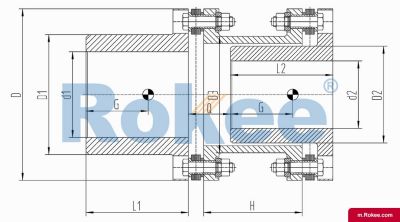
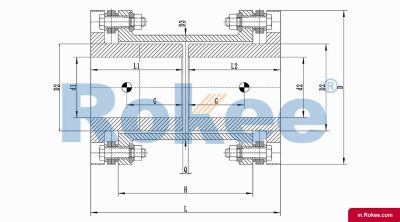
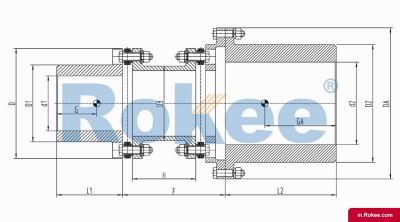
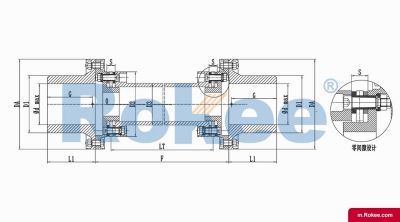
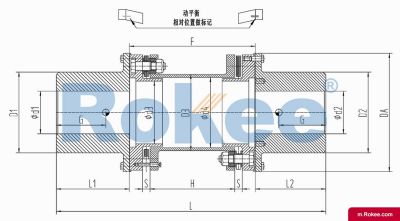
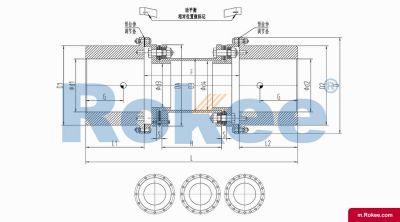
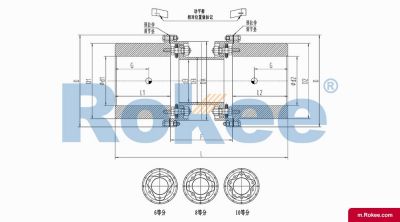
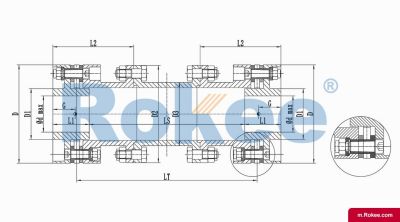
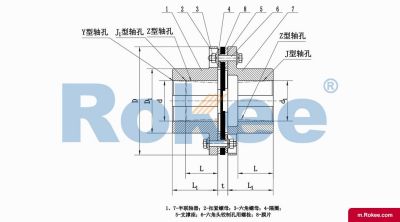
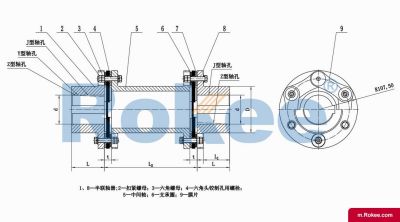
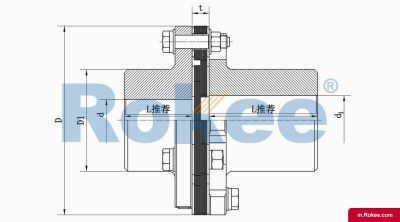
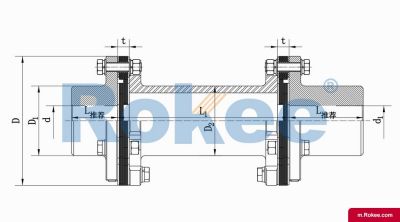
Membrane Coupling is a type of coupling, which is composed of several sets of diaphragms connected to two halves of the coupling by bolts in a staggered manner. Each set of diaphragms is composed of several stacked pieces, and the relative displacement of the two shafts connected is compensated by the elastic deformation of the diaphragms. It is a high-performance metal strong element flexible coupling.
There are various types of Membrane Couplings, and the following are some common ones:
Single Membrane Coupling: made of all stainless steel material, corrosion-resistant, high torsional rigidity, suitable for all motors.
Double Membrane Coupling: Compared to the single diaphragm structure, the double diaphragm has greater flexibility and better ability to compensate for eccentric angles; At the same time, it has higher rigidity and better insulation performance, suitable for all motors.
Step type Membrane Coupling: commonly used in working conditions with high torque.
Keyless Membrane Coupling: This is a new product of Membrane Coupling, which adopts expansion locking method and outstanding impact resistance performance.
In addition, there are some specially designed Membrane Couplings, such as long-span Membrane Couplings, which have a clamping separation structure, are made of aviation materials, have high transmission torque, and can be customized in length, suitable for pumps and frame systems.
There are various types of Membrane Couplings, each with its unique characteristics and applicable range. When choosing, it is necessary to comprehensively consider factors such as actual working conditions, transmission requirements, and economy.
In the complex ecosystem of industrial power transmission, membrane couplings stand out as critical components that bridge the gap between power sources and driven machinery, ensuring efficient torque transfer while accommodating inevitable shaft misalignments. Unlike traditional coupling solutions that rely on lubrication or elastic materials prone to degradation, membrane couplings leverage the elastic deformation of metallic diaphragms to achieve reliable power transmission, making them indispensable in high-precision, high-speed, and harsh operating environments.
The core working principle of a membrane coupling revolves around the elastic deformation of its diaphragm components, which enables torque transmission while compensating for axial, radial, and angular misalignments between connected shafts. A typical membrane coupling consists of two half-couplings and one or more sets of diaphragms. The half-couplings are designed to connect to the drive shaft (e.g., from an electric motor or turbine) and the driven shaft (e.g., of a pump, compressor, or gearbox), respectively, while the diaphragms are clamped between the half-couplings using bolts arranged in a circular pattern. When the drive shaft rotates, torque is transmitted from one half-coupling to the diaphragms. Under the action of torque, the diaphragms undergo controlled bending deformation, which allows the torque to be smoothly transferred to the other half-coupling and ultimately to the driven machinery. This deformation mechanism is crucial because it eliminates the need for direct mechanical contact between moving parts, thereby avoiding friction, wear, and the associated maintenance requirements of lubricated couplings.
The diaphragms, as the core elastic elements of the coupling, are typically fabricated from high-strength, corrosion-resistant metallic materials such as stainless steel. The choice of stainless steel is not arbitrary; its high tensile strength ensures that the diaphragms can withstand large torque loads without permanent deformation, while its corrosion resistance enables the coupling to operate in harsh environments containing moisture, chemicals, or salt spray. The geometric design of the diaphragms also plays a pivotal role in their performance. Common designs include hyperbolic, polygonal, and spoke-type configurations. Hyperbolic diaphragms, for instance, offer excellent flexibility and can accommodate larger angular and axial misalignments, making them suitable for applications where shaft alignment is challenging. Polygonal diaphragms, on the other hand, provide higher torsional stiffness, which is essential for high-precision transmission systems that require minimal angular deviation during operation. Spoke-type diaphragms, with their distributed stress design, excel in high-torque applications by reducing stress concentration points, thereby extending the fatigue life of the coupling.
One of the most prominent advantages of membrane couplings is their exceptional misalignment compensation capability. In industrial settings, perfect shaft alignment is nearly impossible to achieve and maintain over time due to factors such as thermal expansion, vibration, foundation settlement, and installation errors. Membrane couplings can effectively compensate for axial misalignment (caused by thermal expansion of shafts), radial misalignment (resulting from bearing wear or misinstallation), and angular misalignment (due to shaft deflection or misalignment between the drive and driven units). This compensation capability not only reduces the mechanical stress on shafts, bearings, and seals but also minimizes vibration and noise, thereby protecting the entire transmission system from premature failure. Compared to gear couplings, which also offer misalignment compensation but require regular lubrication and are prone to oil leakage, membrane couplings provide a cleaner and more reliable solution, especially in applications where contamination must be avoided, such as food processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and semiconductor production.
Another key advantage of membrane couplings is their high transmission efficiency. Thanks to their all-metal construction with no sliding or rotating contact between parts, membrane couplings experience minimal energy loss during torque transfer. Studies have shown that the transmission efficiency of membrane couplings can reach up to 99.86%, which is significantly higher than that of gear couplings (typically 98-99%) and some elastic couplings. This high efficiency translates to energy savings, reduced operational costs, and improved overall system performance, making membrane couplings an ideal choice for energy-intensive industries such as power generation, oil and gas, and heavy manufacturing. Additionally, the all-metal design of membrane couplings ensures excellent high-temperature resistance, allowing them to operate in environments with temperatures ranging from -50°C to 300°C or higher, depending on the material used. This is a distinct advantage over elastic couplings, which often use rubber or plastic components that degrade at high temperatures, limiting their applicability in high-temperature processes such as chemical reactions, metal smelting, and steam turbine systems.
Maintenance-free operation is another critical benefit that sets membrane couplings apart from many other coupling types. Traditional couplings such as gear couplings and chain couplings require regular lubrication to reduce friction and wear, which involves additional costs for lubricants, labor, and downtime. In contrast, membrane couplings have no moving parts that require lubrication, and their metallic diaphragms are resistant to wear and tear under normal operating conditions. This "fit and forget" characteristic not only reduces maintenance costs but also increases the reliability and availability of the equipment, as there is no risk of lubricant leakage, contamination, or lubrication-related failures. In industries where downtime can result in substantial financial losses, such as oil refineries, power plants, and continuous production lines, the maintenance-free nature of membrane couplings is particularly valuable.
The compact and lightweight design of membrane couplings is also worthy of note. Compared to gear couplings of the same torque capacity, membrane couplings are typically smaller in size and lighter in weight. This compact design makes them suitable for applications where space is limited, such as in small-scale industrial machinery, precision equipment, and automotive powertrains. The reduced weight also contributes to lower inertial forces during high-speed operation, which minimizes vibration and improves the dynamic balance of the transmission system. High dynamic balance is crucial for high-speed applications such as centrifuges, turbochargers, and high-speed pumps, where even minor imbalances can cause severe vibration, leading to bearing damage, seal failure, and structural fatigue. Membrane couplings are often manufactured with high-precision machining processes and undergo dynamic balance testing to meet strict balance grades such as G6.3 or higher, ensuring stable operation at speeds of up to 22,000 rpm or more.
When selecting a membrane coupling for a specific application, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and reliability. First and foremost is the torque requirement. The coupling must be capable of transmitting the maximum continuous torque generated by the drive source, as well as accommodating occasional peak torque loads without failure. It is essential to consider the torque fluctuation characteristics of the application, as shock loads or cyclic torque can significantly affect the fatigue life of the diaphragms. Second, the misalignment parameters of the system must be evaluated, including the maximum axial, radial, and angular misalignments expected during operation. Choosing a coupling with sufficient misalignment compensation capability ensures that the diaphragms do not undergo excessive deformation, which can lead to premature fatigue failure.
Material selection is another critical aspect of membrane coupling selection. The choice of diaphragm material depends on the operating environment and application requirements. For general industrial applications, 304 stainless steel is commonly used due to its good strength and corrosion resistance. In more demanding environments, such as those containing chloride ions (e.g., marine applications or chemical plants using saltwater), 316L stainless steel is preferred for its superior corrosion resistance. For high-temperature applications, special alloys such as Inconel may be used to maintain strength and flexibility at elevated temperatures. Additionally, the design of the half-couplings should be considered; they are typically made from carbon steel, alloy steel, or aluminum alloy, depending on the torque requirements and weight constraints of the application.
The operating speed is also a key consideration, as it affects the dynamic balance and fatigue life of the coupling. High-speed applications require couplings with precise dynamic balance to minimize vibration, and the diaphragms must be designed to withstand the centrifugal forces generated at high speeds. Furthermore, environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, chemical exposure, and dust levels must be taken into account to ensure that the coupling materials do not degrade over time. For example, in food processing or pharmaceutical applications, where hygiene is critical, the coupling must be made from materials that are easy to clean and resistant to sanitizing agents. In hazardous environments such as oil refineries or coal mines, spark-resistant designs (using non-ferrous components) may be required to prevent ignition of flammable gases or dust.
Membrane couplings find widespread application across a diverse range of industries, thanks to their versatile performance characteristics. In the oil and gas industry, they are extensively used in pumps, compressors, and turbines for offshore and onshore operations. The corrosion resistance and high-pressure tolerance of membrane couplings make them ideal for these applications, where equipment is often exposed to saltwater, corrosive chemicals, and extreme pressure conditions. For example, in offshore oil platforms, membrane couplings connect the main engines to the propellers and auxiliary systems, ensuring reliable power transmission in harsh marine environments.
The power generation industry is another major user of membrane couplings. They are used in thermal power plants to connect steam turbines to generators, as well as in hydropower plants for connecting water turbines to generators. In wind power generation, membrane couplings play a crucial role in connecting the wind turbine rotor to the gearbox and generator, withstanding the variable torque loads and misalignments caused by wind turbulence. The high reliability and maintenance-free operation of membrane couplings are particularly important in wind farms, which are often located in remote areas with difficult access, making maintenance work costly and time-consuming. Studies have shown that membrane couplings used in boiler feed pumps of power plants can achieve operating hours exceeding 120,000, demonstrating their exceptional durability.
In the mechanical manufacturing industry, membrane couplings are widely used in high-precision equipment such as CNC machine tools, printing machinery, and robotic systems. The high torsional stiffness and zero backlash of membrane couplings ensure precise torque transmission, which is essential for achieving high machining accuracy in CNC lathes and milling machines. In robotic arms, membrane couplings enable smooth and accurate movement by minimizing angular deviation, ensuring that the robot can perform precise tasks such as assembly, welding, and material handling. Additionally, in the automotive industry, membrane couplings are used in electric vehicle powertrains, where their compact size, high efficiency, and low vibration contribute to improved vehicle performance and energy efficiency.
The chemical and pharmaceutical industries also benefit greatly from the use of membrane couplings. In chemical processing plants, they are used in pumps, mixers, and agitators that handle corrosive chemicals, where the corrosion-resistant properties of stainless steel diaphragms prevent material degradation and contamination. In pharmaceutical manufacturing, the clean, lubrication-free design of membrane couplings ensures compliance with strict hygiene standards, as there is no risk of lubricant leakage contaminating drugs or production equipment. Similarly, in the food and beverage industry, membrane couplings are used in processing lines for dairy, beverages, and canned foods, where easy cleaning and resistance to sanitizing agents are essential.
When comparing membrane couplings with other types of couplings, their unique combination of advantages becomes even more apparent. Compared to elastic couplings (which use rubber or plastic elements), membrane couplings offer higher temperature resistance, longer service life, and better torsional stiffness, although they have slightly lower vibration damping capabilities. Elastic couplings are more suitable for low-speed, low-torque applications where vibration damping is a primary concern, while membrane couplings are preferred for high-speed, high-precision applications. Compared to gear couplings, membrane couplings are lighter, more compact, require no lubrication, and produce less noise, although gear couplings can transmit higher torque in some cases. Gear couplings are typically used in heavy-duty, low-speed applications such as mining machinery and steel mills, where maximum torque transmission is prioritized over maintenance convenience.
Despite their numerous advantages, membrane couplings are not without limitations. One of the main limitations is their relatively higher initial cost compared to some traditional couplings. However, this higher upfront cost is often offset by lower maintenance costs, longer service life, and improved energy efficiency over the coupling's lifecycle. Another limitation is their limited vibration damping capability. In applications where severe vibration is present (e.g., from unbalanced machinery or shock loads), additional vibration damping measures may be required to protect the transmission system. Additionally, membrane couplings are susceptible to damage if subjected to excessive misalignment or overload beyond their design limits. Therefore, proper installation, alignment, and load calculation are essential to ensure their reliable operation.
Looking ahead, the development of membrane couplings is likely to be driven by advancements in material science and manufacturing technology. The use of advanced composite materials and nanotechnology may further enhance the strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance of diaphragms, enabling membrane couplings to operate in even more extreme environments. Improvements in precision machining and 3D printing technology may also lead to more complex and optimized diaphragm designs, further improving their performance and reducing production costs. Additionally, with the growing trend toward industrial automation and smart manufacturing, membrane couplings may be integrated with sensors to monitor their operating status (e.g., temperature, vibration, and torque), enabling predictive maintenance and further improving the reliability of transmission systems.
In conclusion, membrane couplings represent a sophisticated and reliable solution for industrial power transmission, offering a unique combination of high efficiency, excellent misalignment compensation, maintenance-free operation, and durability. Their all-metal construction and elastic deformation mechanism make them suitable for a wide range of applications, from high-precision CNC machines to harsh offshore oil platforms. By understanding the fundamental principles, performance advantages, and selection criteria of membrane couplings, engineers and industrial operators can make informed decisions that enhance the efficiency, reliability, and longevity of their transmission systems. As material and manufacturing technologies continue to advance, membrane couplings are poised to play an even more important role in the future of industrial power transmission, supporting the development of more efficient, sustainable, and intelligent manufacturing processes.
« Membrane Couplings » Update Date: 2026/1/10
URL: https://m.rokee.com/tags/membrane-couplings.html