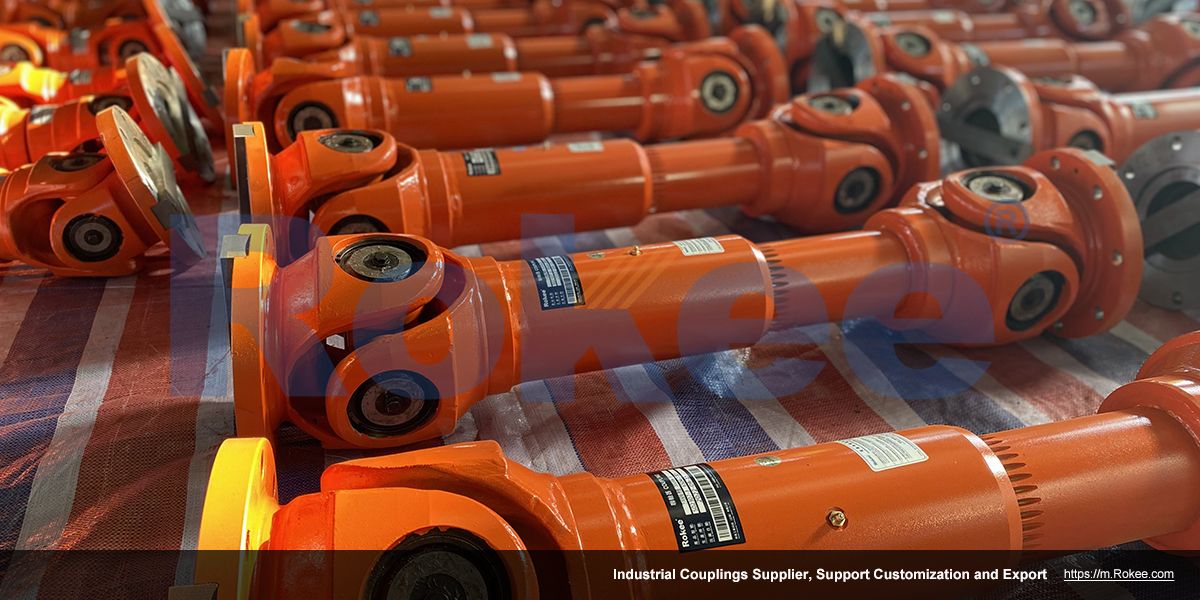
Rokee is a chinese Universal Couplings Manufacturer, provide Universal Couplings processing and customization services, Over the years, with excellent quality, we have been continuously providing many coupling products of various categories and uses complying with multiple standards and a full range of services, from the Universal Couplings selection to final installation and operation, for the industry fields of ferrous metallurgy, nuclear power, gas turbine, wind power, ropeway construction, lifting transportation, general equipment, etc. We strictly comply with quality system requirements and implement the whole process control to become a reliable and trustworthy partner of customers.
Providing customers with better Universal Couplings is always our driving force. Our aim is to transmit power for you and generate value for both of us. We look forward to joining you and becoming your partner for common progress.
-
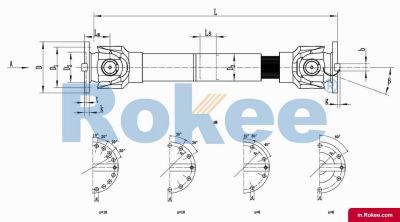
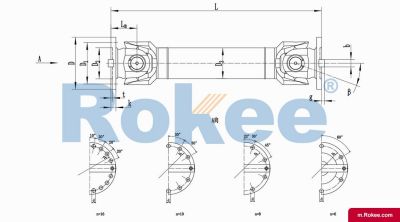
SWC-BH Cardan Shaft
SWC-BH standard telescopic welded universal joint couplingView More -
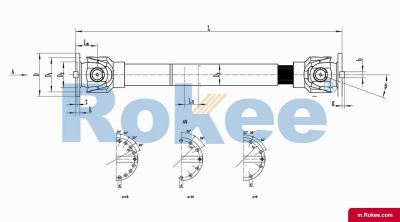
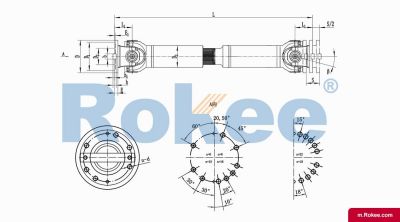
SWC-CH Cardan Shaft
SWC-CH long telescopic welded universal joint couplingView More -
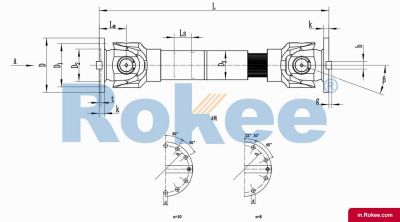
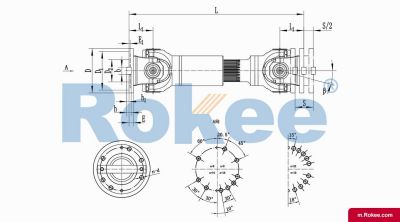
SWC-DH Cardan Shaft
SWC-DH short telescopic welded universal joint couplingView More -
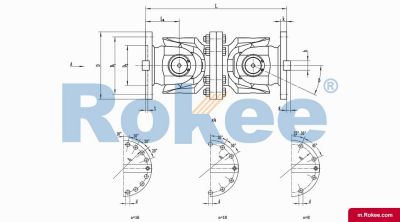
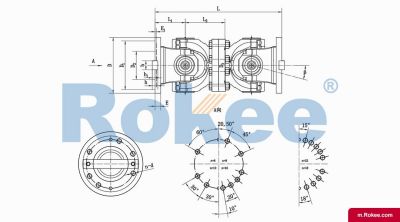
SWC-WD Cardan Shaft
SWC-WD non-telescopic short universal joint couplingView More -
SWC-WH Cardan Shaft
SWC-WH non-telescopic welded universal joint couplingView More -
SWP-A Cardan Shaft
SWP-A telescopic long type universal joint couplingView More -
SWP-B Cardan Shaft
SWP-B telescopic short type universal joint couplingView More -
SWP-C Cardan Shaft
SWP-C non telescopic short type universal joint couplingView More -
SWP-D Cardan Shaft
SWP-D non telescopic long type universal joint couplingView More
Universal Coupling is a mechanism that utilizes the characteristics of its mechanism to enable continuous rotation of the two shafts connected without being on the same axis and with an angle between the axes, and to reliably transmit torque and motion. It has a large angular compensation capability, compact structure, and high transmission efficiency. There are various structural types of universal couplings, such as cross shaft type, ball cage type, ball fork type, convex block type, ball pin type, ball joint type, ball joint plunger type, three pin type, trident rod type, three ball pin type, hinge rod type, etc. Among them, the most commonly used is the cross axis type, followed by the cage type. The core component of the cross axis Universal Coupling is the cross axis, which allows the two shafts to rotate continuously at equal angular velocities within a large range of angles. The ball cage Universal Coupling achieves two axis transmission through components such as the outer ring of the ball cage, the inner ring of the star shape, the cage, and the transmission steel ball. It is suitable for working conditions with large inclination angles and limited radial dimensions.
According to the magnitude of the transmitted torque, universal couplings can be classified as heavy, medium, light, and small. Different models of universal couplings are suitable for different mechanical transmission systems. Universal couplings are widely used in metallurgy, heavy machinery, petrochemicals, engineering machinery, rail transportation, agricultural machinery, industrial machinery and other fields. For example, in steel rolling machinery, universal couplings are used to connect rollers and transmission systems, achieving reliable torque transmission; In heavy transportation equipment, it is used to connect the wheels and transmission shaft, ensuring that the vehicle can travel smoothly in various road conditions.
Universal couplings have significant angular compensation capabilities and can adapt to changes in the angle between two shafts. Compact structure, small footprint, easy to install and maintain. The transmission efficiency of universal couplings is high, which can reduce energy loss and improve the overall performance of mechanical transmission systems. Using high-quality materials and advanced manufacturing processes, the Universal Coupling has high reliability and durability.
When selecting a Universal Coupling, factors such as the magnitude of the transmitted torque, the speed of the shaft, and the magnitude and direction of the relative displacement between the two shafts need to be considered. At the same time, it is necessary to refer to the characteristics of various types of couplings and choose a suitable type of coupling. For the universal couplings that have already been selected, regular maintenance and upkeep are required. For example, regular lubrication can extend its service life; When disassembling and reinstalling, it is necessary to pay attention to adjusting the position of the cross axis to balance wear and tear; In addition, it is necessary to regularly check the wear of the coupling and replace damaged components in a timely manner.
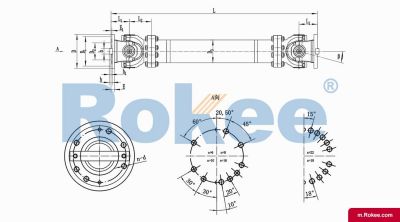
A universal coupling, also commonly referred to as a universal joint or U-joint, is a critical mechanical component designed to connect two rotating shafts whose axes are inclined to each other at an angle. Its primary function is to transmit rotational power and torque between these misaligned shafts while accommodating various forms of misalignment, including angular, axial, and radial deviations. This unique capability makes it an indispensable element in numerous mechanical systems across diverse industries, enabling flexible power transmission that would otherwise be challenging or impossible with rigid connections. The fundamental design of a universal coupling revolves around a set of hinges or pivots that allow for rotational movement between the connected shafts, ensuring continuous power transfer even when the relative position of the shafts changes dynamically during operation.
The basic structure of a universal coupling typically consists of several key components: two yokes, a cross-shaped central member (often called a cross or spider), and bearings. The yokes are mechanical fixtures attached to the ends of the two shafts that need to be connected; each yoke features a pair of ears with holes designed to accommodate the bearings. The cross-shaped central member, which is the core of the coupling, has four arms (trunnions) that fit into the bearing-mounted holes of the yokes. The bearings, usually needle bearings due to their compact size and high load-bearing capacity, reduce friction between the cross trunnions and the yoke ears, enabling smooth rotational movement and efficient torque transmission. This modular structure not only facilitates easy assembly and disassembly but also ensures that the coupling can withstand the mechanical stresses associated with torque transfer and misalignment compensation. Depending on the specific application requirements, variations in this basic structure may exist, such as the addition of sealing devices to prevent lubricant leakage and protect internal components from contaminants, or the use of integral forging for critical parts to enhance structural integrity.
There are several distinct types of universal couplings, each tailored to specific application scenarios based on their structural characteristics and performance capabilities. The most common type is the Hooke's joint, also known as the Cardan joint, which is a single universal joint consisting of two yokes and a cross member. This type is widely used due to its simplicity, compact size, and cost-effectiveness, and it can accommodate angular misalignment angles typically ranging from 5° to 45° depending on the design. However, a key limitation of the single Hooke's joint is its non-uniform velocity transmission: when the input shaft rotates at a constant speed, the output shaft speed fluctuates periodically, which can cause vibration and additional stress on the connected machinery. To address this issue, the double universal joint (or double Cardan joint) is often employed, which consists of two single universal joints connected by an intermediate shaft, oriented 90° out of phase with each other. This configuration ensures that the velocity fluctuations from the first joint are canceled out by the second, resulting in constant velocity transmission between the input and output shafts, making it suitable for applications requiring smooth power transfer, such as automotive drivetrains and precision machinery.
Other specialized types of universal couplings include the Rzeppa joint, a constant-velocity joint that uses a cage and ball bearings to maintain uniform speed even at large angular misalignments, commonly found in front-wheel-drive vehicles. The Oldham coupling, another variant, consists of three disks (one central and two outer) with perpendicular slots, allowing for significant parallel misalignment while minimizing torque fluctuations, and is often used in printing presses and paper mills where shock absorption is essential. Beam couplings, which feature a flexible steel beam connecting two shaft hubs, are lightweight and compact, making them ideal for space-constrained applications such as medical equipment and robotics. Each type of universal coupling has its unique advantages and limitations, with the selection depending on factors such as the required misalignment compensation, torque capacity, rotational speed, operating environment, and space constraints.
The working principle of a universal coupling centers on the ability of its components to accommodate misalignment while transmitting torque. When torque is applied to the input shaft, the motion is transferred through the input yoke to the cross member. The cross member, via its trunnions and bearings, then transmits this rotational motion to the output yoke and ultimately to the output shaft. The hinges formed by the cross trunnions and bearings allow the yokes to rotate relative to each other, enabling the coupling to compensate for angular misalignment between the two shafts. In the case of axial misalignment (where the shafts are offset along their axial direction), some universal coupling designs, such as those with telescoping shafts, can accommodate this by allowing relative movement between the components. Radial misalignment (where the shafts are offset radially) is also compensated for through the flexible movement of the coupling's components. The efficiency of torque transmission in a universal coupling is relatively high, typically above 90% for well-maintained units, as the design minimizes energy loss through friction, especially with the use of high-quality bearings and proper lubrication.
The material selection for universal couplings is a critical factor that directly impacts their performance, durability, and suitability for specific operating environments. The most commonly used materials include various types of steel, aluminum alloys, and specialized composites. Steel, particularly alloy steels such as 40Cr and 42CrMo, is widely used for heavy-duty applications due to its high strength, toughness, and wear resistance. These alloy steels are often subjected to heat treatment processes such as quenching and tempering to achieve a balance of hardness and ductility, making them ideal for use in冶金 machinery, mining equipment, and other high-torque applications. Stainless steel, such as 304 and 316 grades, is preferred for applications in corrosive environments, such as marine equipment, food processing machinery, and chemical plants, due to its excellent corrosion resistance. 316 stainless steel, in particular, offers enhanced resistance to chloride corrosion, making it suitable for marine and offshore applications.
Aluminum alloys are used in applications where lightweight construction is a priority, such as aerospace components, drones, and automated production lines. The low density of aluminum (approximately one-third that of steel) reduces the overall weight of the machinery, improving energy efficiency and maneuverability, although aluminum has lower torque-bearing capacity compared to steel. Specialized composite materials, such as carbon fiber-reinforced polymers, are used in high-performance applications such as aerospace and racing vehicles, where extreme lightweight and high fatigue resistance are required. However, these composite materials are typically more expensive and difficult to process, limiting their use to niche applications. Other materials, such as nylon-coated metals, are used in precision instruments to provide additional shock absorption and noise reduction, with the metal core ensuring structural integrity and the nylon coating minimizing vibration.
Universal couplings find applications across a wide range of industries, owing to their versatility and ability to accommodate misalignment. In the automotive industry, they are a key component of drivetrains, connecting the transmission to the drive axle and allowing for the vertical movement of the suspension while transmitting power from the engine to the wheels. Double universal joints are commonly used in rear-wheel-drive vehicles to ensure constant velocity transmission, while front-wheel-drive vehicles often use constant-velocity universal joints such as Rzeppa joints to handle the combined steering and power transmission requirements. In the industrial machinery sector, universal couplings are used in conveyor systems, pumps, compressors, and machine tools, where they connect motors to driven components and compensate for misalignments caused by installation errors or thermal expansion.
Heavy industries such as metallurgy, mining, and construction rely heavily on robust universal couplings to handle high torque loads and harsh operating conditions. For example, in rolling mills, large universal couplings transmit power from the drive motors to the rolls, accommodating the dynamic misalignments that occur during the rolling process. Construction machinery such as excavators and loaders use universal couplings in their hydraulic systems and drivetrains, enabling flexible power transmission in compact spaces. The marine industry uses stainless steel universal couplings in ship propulsion systems, connecting the engine to the propeller shaft and withstanding the corrosive effects of saltwater. The aerospace industry employs lightweight aluminum and composite universal couplings in aircraft control systems and engine components, where reliability and weight reduction are critical factors. Even in precision applications such as medical equipment and robotics, small and lightweight universal couplings ensure smooth and accurate motion transmission.
Like any mechanical component, universal couplings have their inherent advantages and limitations. One of the primary advantages is their excellent angular misalignment compensation capability, which far exceeds that of rigid couplings and many flexible couplings, making them ideal for applications where shaft alignment is dynamic or difficult to maintain. They also have high torque transmission capacity, especially when constructed from high-strength alloys, and can handle heavy loads in industrial applications. Their compact and lightweight design, particularly in smaller sizes, makes them suitable for installations where space is limited. Additionally, universal couplings offer high transmission efficiency, with minimal energy loss due to friction when properly lubricated, and can adapt to a wide range of operating temperatures and environments, from high-temperature industrial processes to cold marine conditions.
However, there are also limitations to consider. As mentioned earlier, single Hooke's joints suffer from non-uniform velocity transmission, which can cause vibration, noise, and additional stress on connected components, requiring the use of double joints for constant velocity applications. Universal couplings also require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The bearings and cross trunnions need periodic lubrication to reduce friction and wear, and seals must be inspected to prevent the ingress of contaminants that can damage internal components. Without proper maintenance, wear and tear can lead to premature failure, resulting in costly downtime. Another limitation is their restricted performance at extremely high rotational speeds; while some specialized designs can handle moderate high speeds, universal couplings are generally not suitable for ultra-high-speed applications due to balance issues and increased vibration. Additionally, high-performance universal couplings, such as constant-velocity joints, can be relatively expensive due to their complex design and precision manufacturing requirements, which may increase the initial cost of equipment.
Proper maintenance and installation are crucial for maximizing the service life and performance of universal couplings. During installation, careful attention should be paid to shaft alignment to minimize unnecessary stress on the coupling components. While universal couplings can accommodate misalignment, excessive misalignment beyond their design limits will significantly increase wear and reduce lifespan. Regular lubrication is essential; the type of lubricant should be selected based on the operating temperature, load, and environment, with periodic re-lubrication schedules established to ensure consistent performance. Seals should be checked regularly for damage or leakage, and replaced promptly to prevent contamination. Routine inspections should include checking for signs of wear, such as excessive play in the joints, corrosion, or damage to the yokes and cross member. If any defects are detected, the coupling should be repaired or replaced immediately to avoid catastrophic failure.
In conclusion, universal couplings are versatile and essential mechanical components that play a vital role in enabling flexible power transmission between misaligned shafts across a wide range of industries. Their diverse types, from simple single Hooke's joints to complex constant-velocity joints, are tailored to meet the specific requirements of different applications, whether it be high torque in heavy industry, precision in robotics, or corrosion resistance in marine environments. The selection of the appropriate universal coupling involves considering factors such as misalignment requirements, torque capacity, rotational speed, operating environment, and material compatibility. With proper design, material selection, installation, and maintenance, universal couplings can provide reliable and efficient performance, ensuring the smooth operation of mechanical systems and minimizing downtime. As technology advances, improvements in materials, manufacturing processes, and design optimization will continue to enhance the performance and versatility of universal couplings, expanding their applications and ensuring their continued importance in the field of mechanical engineering.
« Universal Couplings » Update Date: 2026/1/10
URL: https://m.rokee.com/tags/universal-couplings.html