Rokee is a chinese Telescoping Driveshafts Manufacturer, provide Telescoping Driveshafts processing and customization services, Over the years, with excellent quality, we have been continuously providing many coupling products of various categories and uses complying with multiple standards and a full range of services, from the Telescoping Driveshafts selection to final installation and operation, for the industry fields of ferrous metallurgy, nuclear power, gas turbine, wind power, ropeway construction, lifting transportation, general equipment, etc. We strictly comply with quality system requirements and implement the whole process control to become a reliable and trustworthy partner of customers.
Providing customers with better Telescoping Driveshafts is always our driving force. Our aim is to transmit power for you and generate value for both of us. We look forward to joining you and becoming your partner for common progress.
-
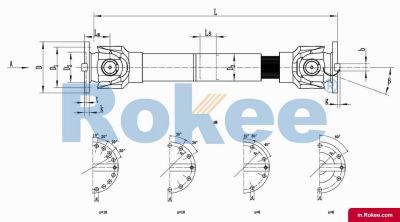
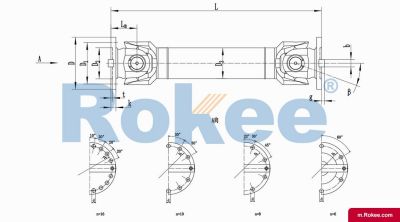
SWC-BH Cardan Shaft
SWC-BH standard telescopic welded universal joint couplingView More -
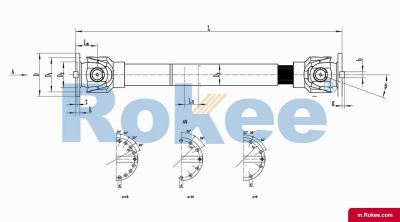
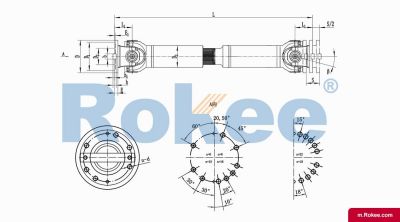
SWC-CH Cardan Shaft
SWC-CH long telescopic welded universal joint couplingView More -
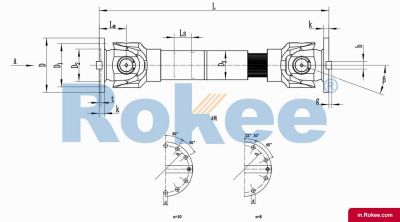
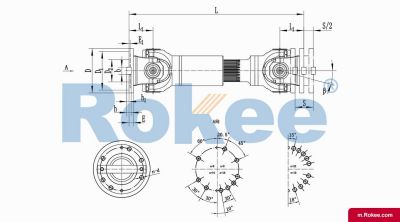
SWC-DH Cardan Shaft
SWC-DH short telescopic welded universal joint couplingView More -
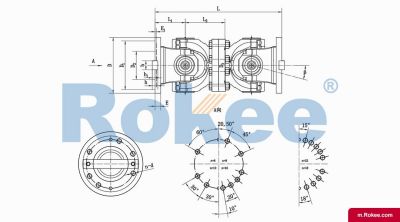
SWC-WD Cardan Shaft
SWC-WD non-telescopic short universal joint couplingView More -
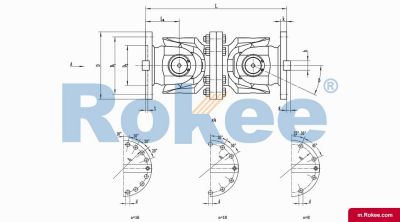
SWC-WH Cardan Shaft
SWC-WH non-telescopic welded universal joint couplingView More -
SWP-A Cardan Shaft
SWP-A telescopic long type universal joint couplingView More -
SWP-B Cardan Shaft
SWP-B telescopic short type universal joint couplingView More -
SWP-C Cardan Shaft
SWP-C non telescopic short type universal joint couplingView More -
SWP-D Cardan Shaft
SWP-D non telescopic long type universal joint couplingView More
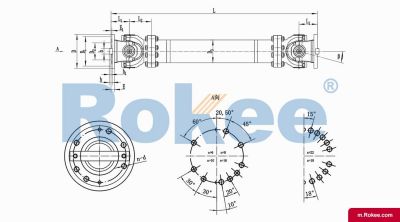
The telescoping driveshaft is a mechanical transmission device that combines the telescoping driveshaft and the telescopic function. It is mainly used to connect transmission systems where two shafts are not in the same straight line and need to compensate for axial displacement. This type of coupling can simultaneously solve the problems of angle deviation and axial displacement compensation, and is an important component in modern mechanical transmission systems.
The core working principle is based on the motion characteristics of the telescoping driveshaft: when the driving shaft rotates, power is transmitted to the driven shaft through the cross axis, allowing for a certain degree of angular deviation between the two shafts (usually 15 ° -45 °). The telescopic function is achieved through a spline shaft or sleeve structure, allowing the coupling to freely expand and contract in the axial direction, compensating for the axial displacement generated during the transmission process.
Main structural components
Cross shaft assembly: composed of a cross shaft, needle roller bearings, and bearing seats, it is the core component for transmitting torque and adapting to angular deviations.
Expansion spline component: usually composed of an internal spline shaft and an external spline sleeve, allowing axial relative sliding while ensuring effective torque transmission.
Flange or end connector: used to connect the drive shaft and the driven shaft, can be designed as flange type, clamping type, or welding type according to needs.
Sealing system: protects internal bearings and splines from contamination and extends their service life.
Lubrication device: including oil nozzle and internal oil passage, ensuring that all moving parts are fully lubricated.
Technical features and advantages
Multi directional compensation capability: simultaneously compensates for radial, angular, and axial deviations, adapting to complex installation conditions.
High transmission efficiency: using precision needle roller bearings with low friction loss, the transmission efficiency can reach over 98%.
Large angle compensation: A single section can achieve angle compensation of 15 ° -45 °, while a double section connected in series can achieve a larger compensation angle.
Axial expansion and contraction: Depending on the model, the expansion and contraction can reach 50-300mm, meeting the requirements of different working conditions.
High speed capability: High dynamic balance level, suitable for high-speed operation scenarios.
Long life design: Made of high-quality alloy steel and special heat treatment process, it has high wear resistance and fatigue strength.
Main application areas
Construction machinery: excavators, loaders, cranes, and other applications that require large angle deflection and axial displacement compensation.
Metallurgical equipment: Long axis transmission for heavy equipment such as rolling mills and straightening machines.
Shipbuilding industry: Ship propulsion shaft system, compensating for hull deformation and installation errors.
Petroleum machinery: field operation equipment such as drilling equipment and pumping units.
Wind power industry: Transmission connection of yaw system for wind turbines.
Special vehicles: Transmission systems for military vehicles, mining vehicles, and other harsh working conditions.
Selection and design considerations
Torque capacity: Calculate the required torque based on the transmitted power and speed, taking into account start-up shock and operating condition factors.
Compensation requirement: Determine the required range of angle compensation and axial expansion and contraction.
Speed limit: Couplings of different specifications have their maximum operating speed limit.
Installation space: Consider matching the external dimensions of the coupling with the equipment space.
Environmental conditions: Factors such as temperature, humidity, and corrosiveness affect material selection and sealing design.
Maintenance requirements: Select lubrication methods and sealing structures based on maintainability requirements.
Key points of maintenance and upkeep
Regular lubrication: Add designated lubricating grease according to the manufacturer's requirements, paying special attention to the lubrication of the spline area.
Check for wear: Regularly inspect the wear of the cross shaft bearings and spline tooth surfaces.
Sealing inspection: Ensure that the sealing components are intact and prevent contaminants from entering.
Alignment inspection: Regularly check the alignment of the shaft system to avoid working at extreme angles for a long time.
Dynamic balance maintenance: It is necessary to regularly check the dynamic balance status in high-speed applications.
Abnormal vibration monitoring: Abnormal vibration is often a precursor to coupling failure.
As a key component in the field of mechanical transmission, the telescoping driveshaft is advancing towards higher performance, longer lifespan, and greater intelligence, providing a more reliable power transmission solution for modern industrial equipment.
« Telescoping Driveshafts » Post Date: 2024/5/6
URL: https://m.rokee.com/tags/telescoping-driveshafts.html