Rokee is a chinese Universal Joints Manufacturer, provide Universal Joints processing and customization services, Over the years, with excellent quality, we have been continuously providing many coupling products of various categories and uses complying with multiple standards and a full range of services, from the Universal Joints selection to final installation and operation, for the industry fields of ferrous metallurgy, nuclear power, gas turbine, wind power, ropeway construction, lifting transportation, general equipment, etc. We strictly comply with quality system requirements and implement the whole process control to become a reliable and trustworthy partner of customers.
Providing customers with better Universal Joints is always our driving force. Our aim is to transmit power for you and generate value for both of us. We look forward to joining you and becoming your partner for common progress.
-
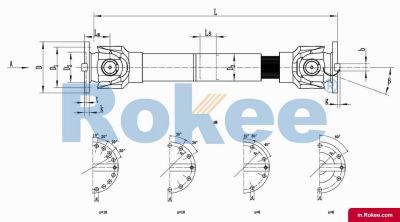
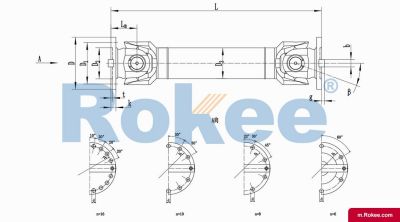
SWC-BH Cardan Shaft
SWC-BH standard telescopic welded universal joint couplingView More -
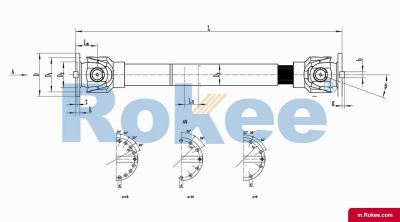
SWC-CH Cardan Shaft
SWC-CH long telescopic welded universal joint couplingView More -
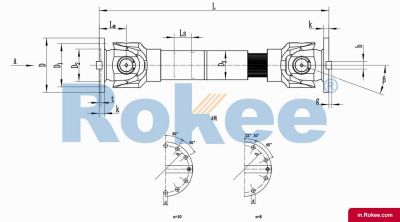
SWC-DH Cardan Shaft
SWC-DH short telescopic welded universal joint couplingView More -
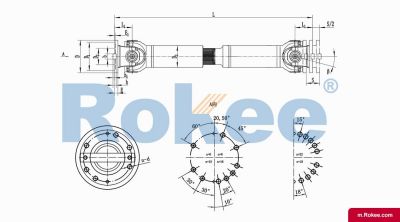
SWC-WD Cardan Shaft
SWC-WD non-telescopic short universal joint couplingView More -
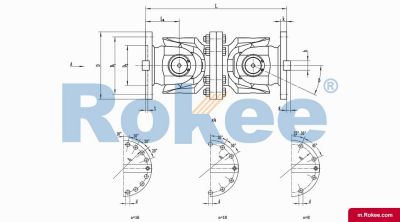
SWC-WH Cardan Shaft
SWC-WH non-telescopic welded universal joint couplingView More -
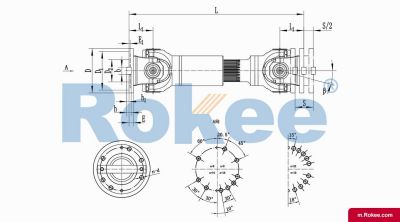
SWP-A Cardan Shaft
SWP-A telescopic long type universal joint couplingView More -
SWP-B Cardan Shaft
SWP-B telescopic short type universal joint couplingView More -
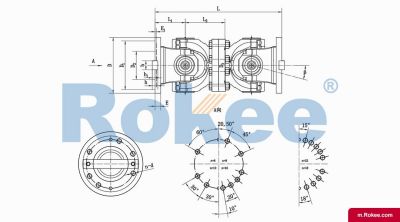
SWP-C Cardan Shaft
SWP-C non telescopic short type universal joint couplingView More -
SWP-D Cardan Shaft
SWP-D non telescopic long type universal joint couplingView More
The universal joint is an indispensable core component in modern mechanical transmission systems. Like the joints of the human body, it can transmit power and motion between axes at different angles. This sophisticated mechanical device is widely used in fields such as automobiles, industrial equipment, aerospace, etc., solving the technical problem of misalignment of the transmission system axis.
The universal joint is essentially a mechanical connection device that enables variable angle power transmission. Its core function is to connect two shafts whose axes are not on the same straight line or whose relative positions constantly change during operation, and reliably transmit rotational motion and torque. This characteristic makes it a "joint" component of the universal transmission system in automobiles, playing a crucial role in situations where the direction of the transmission axis needs to be changed.
The universal joint allows the two connected shafts to deflect relative to each other within a certain angle range (usually up to 45 °) through a special hinge structure. When the driving shaft rotates, the driven shaft is driven to rotate through intermediate elements such as cross shafts or ball cages, while compensating for the angular deviation between the two shafts. This design perfectly solves the problem of traditional rigid connections being unable to transmit motion when the axis is misaligned.
The most significant feature of a universal joint is its ability to continuously transmit power when the angle between the shafts changes. In automotive applications, when the front wheel is both the driving wheel and needs to be turned, the universal joint allows for a large angular deviation between the driving shaft and the wheel shaft (when turning), while ensuring uninterrupted power. This feature also makes it an ideal choice for connecting the differential and wheels in independent suspension systems.
According to their working principles and structural differences, universal joints can be divided into three categories: rigid universal joints (including non constant velocity, quasi constant velocity, and constant velocity), flexible universal joints, and special universal joints. Each type has its unique structural characteristics and applicable scenarios.
Rigid universal joint
Non constant velocity universal joint (cross axis type)
Structural composition: Composed of a cross shaft, two universal joint forks, needle roller bearings, and seals, it is the most common type of rigid universal joint. The four end necks of the cross shaft are connected to the universal joint fork through needle roller bearings, allowing the two shafts to swing relative to each other.
Working principle: When there is an angle between the two axes, the constant rotation of the driving shaft will cause the instantaneous angular velocity of the driven shaft to change periodically, but the average speed remains the same. This non-uniform characteristic generates additional vibration, so a double universal joint combination is often used to counteract this effect.
Performance parameters: allowing a maximum axle angle of 15 ° -20 °, with a transmission efficiency of up to 98% -99%, widely used in the transmission shafts of trucks and off-road vehicles.Quasi constant velocity universal joint
Including types such as double coupling and triple pin shaft, approximate constant speed transmission is achieved through special structural design:
Dual universal joint: Compact combination of two cross axis universal joints, minimizing the length of the transmission shaft through a dual fork structure. Its core feature is that the angle difference between the centerline of the two cross shafts and the axis of the 20000 directional fork is extremely small, thus achieving quasi constant speed transmission. Allowable inter axle angle of up to 50 °, commonly used for steering drive axles.
Three pin universal joint: composed of a main and driven eccentric shaft fork, two three pin shafts, and six bearings, forming three axes Q1-Q1 ', Q2-Q2', and R-R '. The biggest feature is that it allows for a 45 ° large angle of intersection, allowing the vehicle to obtain a smaller turning radius, but with a larger space occupation.constant velocity joint
The universal joint that truly achieves equal instantaneous angular velocity of input and output shafts mainly includes:
Ball cage universal joint: composed of star shaped sleeve, spherical shell, steel ball, and cage. Six steel balls transmit force between the inner and outer raceways, and the cage ensures that the steel balls are in the same plane. According to whether it can expand and contract axially, it can be divided into:
Fixed type (RF section): Maximum deflection angle of 47 °, six steel balls transmit force simultaneously under all working conditions, with strong load-bearing capacity.
Expansion type (VL section): The inner and outer raceways are cylindrical, allowing for axial displacement and eliminating the need for sliding splines, with a maximum deflection angle of 47 °.
Ball fork universal joint: divided into arc raceway type and straight groove raceway type. The former consists of a ball fork with curved grooves and a steel ball, allowing for a deviation angle of 32 ° -33 °; The latter groove type is a straight groove, allowing a 20 ° deflection angle and compensating for axial sliding.
Constant velocity principle: Based on the geometric principle that the point of force transmission is always located on the bisector of the angle between the two axes, similar to the meshing of bevel gears. The cage type achieves this condition through the concentric design of the inner and outer spherical surfaces of the cage, while the fork type is ensured through special raceway geometry.
Flexible universal joint
Relying on the deformation of elastic components such as rubber and polyurethane to compensate for axial deviation, the main features include:
Allow small angle deviations of 3 ° -5 ° and slight axial displacement
No lubrication required, able to absorb impact and attenuate vibration
Simple structure, commonly used for connecting engines and transmissions
Typical structures include rubber metal sleeves or hexagonal rubber ring components
Precision universal joint
Specially designed for high-precision transmission requirements, main features:
Axial angle ≤ 45 °, transmitted torque 11.2-1120N · m
Divided into two structures: single section (WSD type) and double section (WS type)
The bearing types can be needle roller bearings (up to 4000rpm) or sliding bearings (up to 1000rpm)
Finished hole H7 precision, customizable keyways, hexagonal holes, etc
« Universal Joints » Post Date: 2023/8/30
URL: https://m.rokee.com/tags/universal-joints.html