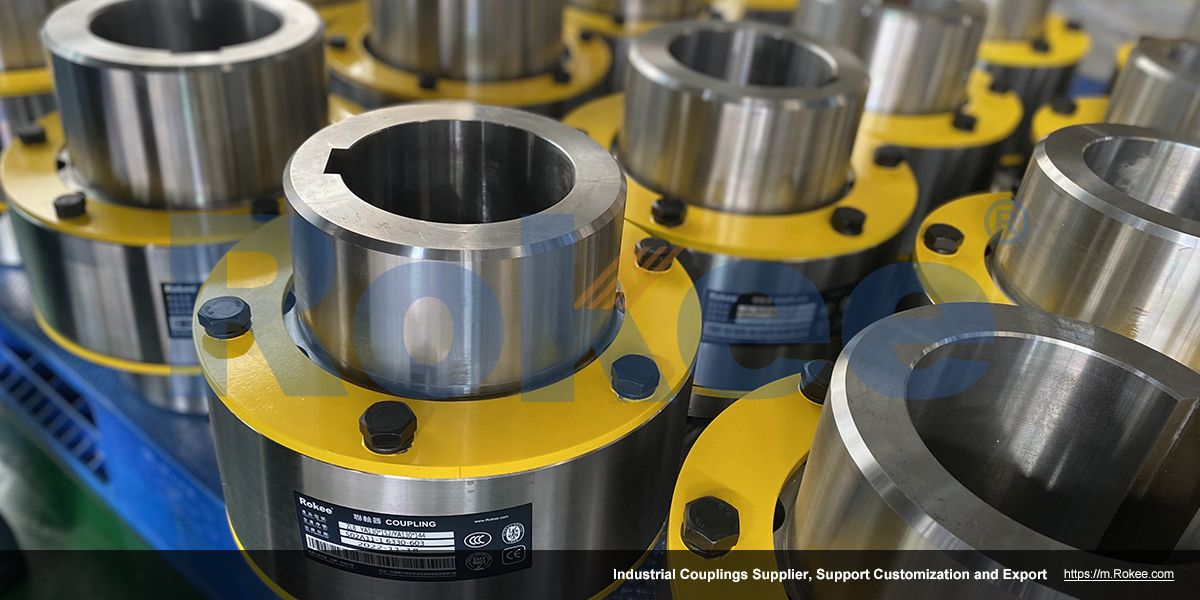
Rokee is a chinese Bushed Couplings Manufacturer, provide Bushed Couplings processing and customization services, Over the years, with excellent quality, we have been continuously providing many coupling products of various categories and uses complying with multiple standards and a full range of services, from the Bushed Couplings selection to final installation and operation, for the industry fields of ferrous metallurgy, nuclear power, gas turbine, wind power, ropeway construction, lifting transportation, general equipment, etc. We strictly comply with quality system requirements and implement the whole process control to become a reliable and trustworthy partner of customers.
Providing customers with better Bushed Couplings is always our driving force. Our aim is to transmit power for you and generate value for both of us. We look forward to joining you and becoming your partner for common progress.
-
LT/TL Elastic Sleeve Pin Coupling
LT Elastic Sleeve Pin Coupling is the basic form of this series of couplings.View More -
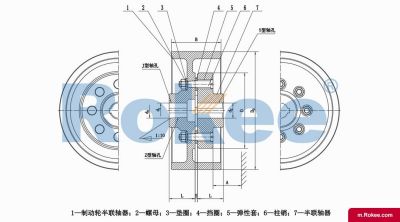
LTZ/TLL Elastic Sleeve Pin Coupling With Brake Wheel
LTZ Elastic Sleeve Pin Coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required.View More
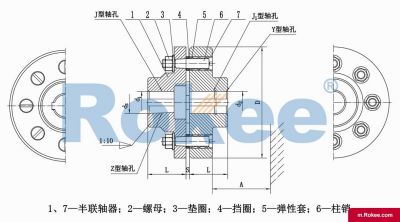
Bushed Coupling is a mechanical transmission device that uses elastic elements to achieve two shaft connection. It is installed in the flange holes of the two half couplings through a column pin with an elastic sleeve (usually made of rubber material) on one end, thereby achieving the connection and torque transmission of the two shafts.
Structurally, the elastic sleeve column pin coupling is mainly composed of two half couplings, column pins, elastic sleeves, and retaining rings. Among them, the elastic sleeve, as a key buffering element, mainly bears compressive deformation during operation and can absorb some vibrations and impacts. Compared with rigid couplings, it has obvious advantages: simple and compact structure, no need for lubrication and maintenance; Easy installation and disassembly, no need to move equipment when replacing elastic components; Has a certain degree of axis offset compensation capability, able to adapt to slight installation errors and work deformations.
However, this type of coupling also has some limitations. Due to the relatively thin thickness of the elastic sleeve, its elastic deformation ability is limited, so the compensation for the relative offset of the two axes is relatively small (the allowable radial displacement is usually 0.14-0.25mm, and the angular displacement is about 0.5 °). At the same time, under conditions of high impact loads or frequent forward and reverse rotation, the elastic sleeve is prone to wear and aging, and its service life will be significantly shortened. It is these characteristics that determine its applicability boundary - it is most suitable for installing small and medium-sized power transmission systems with good base rigidity, high centering accuracy, and low impact loads.
The core design of the Bushed Coupling is reflected in its exquisite structural arrangement. Two half couplings are usually precision cast from cast iron (HT20-40) or cast steel (ZG35II), with sufficient strength and stiffness. Multiple pin holes are evenly distributed on the flange of the coupling, and one end of the pin installed in the hole is equipped with an elastic sleeve, while the other end is fixed with a nut. This arrangement enables the coupling to absorb vibrations and compensate for deviations through the deformation of the elastic sleeve while transmitting torque.
The torque transmission mechanism can be divided into three stages: firstly, the drive side half coupling transmits torque to the elastic sleeve through the column pin; Then, the elastic sleeve undergoes elastic deformation and transmits the force to the driven side column pin; Finally, the driven side column pin drives the other half of the coupling to rotate. During this process, the compression deformation of the elastic sleeve stores some energy and serves as a buffer and shock absorber.
In the complex ecosystem of mechanical power transmission, couplings serve as the critical link that connects rotating shafts, enabling the seamless transfer of torque from a driving source to a driven load. Among the diverse range of couplings available, the bushed coupling stands out for its unique combination of simplicity, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making it a staple in numerous industrial and mechanical applications. This component is specifically designed to address the challenges of shaft misalignment, vibration dampening, and torque transmission while maintaining ease of installation and minimal maintenance requirements.
At its core, a bushed coupling is a type of flexible coupling that consists of several key components working in tandem to achieve efficient power transmission. The fundamental structure typically includes two flanged hubs, a series of pins, and elastomeric bushes. The hubs, which are usually cylindrical in shape with a flange at one end, are designed to be mounted on the respective shafts that need to be connected. These hubs are equipped with evenly spaced holes around the flange circumference, which are sized to accommodate the pins and bushes. The pins, often made of high-strength metallic materials, pass through the holes in both flanges, creating a physical connection between the two hubs. The elastomeric bushes, which are the defining feature of this coupling type, are inserted between the pins and the hub holes, acting as a flexible interface that absorbs vibration and compensates for misalignment. In some variations, additional components such as spacer sleeves, brake wheels, or locking mechanisms may be integrated to meet specific application requirements, but the basic configuration of hubs, pins, and bushes remains consistent across most designs.
The working principle of a bushed coupling revolves around the transfer of torque through the mechanical connection of its components, while leveraging the flexibility of the elastomeric bushes to accommodate misalignment and dampen vibrations. When the driving shaft rotates, it imparts rotational force to the corresponding hub. This rotational force is then transmitted to the pins inserted in the hub's flange holes. As the pins rotate, they exert pressure on the elastomeric bushes, which in turn transfer the torque to the second hub connected to the driven shaft. The elastomeric material of the bushes plays a pivotal role here: as the shafts rotate, any minor misalignment between them causes the bushes to deform elastically. This elastic deformation allows the coupling to accommodate three types of misalignment: angular misalignment (where the shafts are not colinear but intersect at a point), parallel misalignment (where the shafts are parallel but offset from each other), and axial misalignment (where the shafts move along their axial direction relative to each other). Additionally, the elastomeric bushes act as a shock absorber, dampening the vibrations generated by the rotating shafts or the driven load. This vibration dampening not only improves the smoothness of operation but also reduces the wear and tear on other components in the mechanical system, such as bearings and gears.
Material selection for bushed couplings is a critical factor that directly impacts their performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. The hubs and pins are typically manufactured from metallic materials selected for their strength, durability, and resistance to wear. Common materials for hubs include carbon steel, stainless steel, and cast iron, with carbon steel being the most widely used due to its balance of strength and cost-effectiveness. Stainless steel is preferred in applications where corrosion resistance is a priority, such as marine or chemical processing environments. Pins are often made from high-tensile steel or bronze, materials that can withstand the shear forces and compressive loads generated during torque transmission. The elastomeric bushes, on the other hand, are made from a variety of flexible materials, including natural rubber, synthetic rubber (such as neoprene or nitrile), and polyurethane. The choice of bush material depends on the application's operating conditions: natural rubber offers excellent flexibility and vibration dampening but may not be suitable for high-temperature or chemical-exposed environments. Synthetic rubbers, on the other hand, provide better resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals, making them ideal for industrial applications where such conditions are prevalent. Polyurethane bushes offer higher durability and load-bearing capacity compared to rubber, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
One of the key advantages of bushed couplings is their simplicity of design, which translates to ease of installation and maintenance. Unlike more complex coupling types that require precise alignment or specialized tools for installation, bushed couplings can be installed with basic hand tools. The two hubs are first mounted on the respective shafts using keyways, set screws, or taper locks, and then the pins and bushes are inserted through the flange holes to connect the hubs. This straightforward installation process reduces downtime during system setup or maintenance. Additionally, bushed couplings are generally maintenance-free, as the elastomeric bushes do not require lubrication. This eliminates the need for regular lubrication schedules, reduces maintenance costs, and avoids the risk of oil contamination in sensitive applications such as food processing or pharmaceutical manufacturing. When maintenance is required, it typically involves replacing the worn bushes, a task that can be completed quickly without disassembling the entire coupling or disconnecting the shafts.
Bushed couplings are versatile components that find applications across a wide range of industries and mechanical systems. Their ability to accommodate misalignment and dampen vibrations makes them particularly suitable for applications involving electric motors, pumps, compressors, and conveyor systems. In industrial machinery, for example, they are commonly used to connect the motor shaft to the pump shaft in pumping systems, where they compensate for minor misalignments that may occur due to thermal expansion, vibration, or installation errors. This ensures efficient power transmission and extends the lifespan of both the motor and the pump. In conveyor systems, which are widely used in manufacturing, mining, and logistics, bushed couplings connect the drive motor to the conveyor belt shaft, absorbing the shocks and vibrations generated by the movement of the belt and the load being transported. This helps to maintain smooth operation and reduce the risk of component failure.
The automotive and marine industries also utilize bushed couplings in various applications. In automotive systems, they can be found connecting the engine shaft to the transmission shaft, where they help to dampen the vibrations generated by the engine and accommodate minor misalignments between the engine and the transmission. In marine applications, bushed couplings are used to connect the engine shaft to the propeller shaft, withstanding the harsh marine environment and compensating for the misalignments that may occur due to the movement of the vessel. Additionally, bushed couplings are used in agricultural machinery such as tractors and harvesters, where they connect the engine to various implements, absorbing the vibrations generated by the machinery's operation in uneven terrain.
While bushed couplings offer numerous advantages, they also have certain limitations that must be considered when selecting a coupling for a specific application. One of the primary limitations is their lower operating speed compared to rigid couplings or gear couplings. The elastomeric bushes have a maximum speed limit, beyond which the centrifugal forces generated by the rotating pins and bushes can cause the bushes to degrade or fail prematurely. For this reason, bushed couplings are most suitable for low to medium speed applications, typically up to 3000 revolutions per minute (RPM), depending on the size and material of the coupling. Another limitation is their lower torque capacity compared to heavy-duty coupling types such as gear couplings or chain couplings. While they can handle moderate torque loads, they are not suitable for high-torque applications such as large industrial turbines or heavy mining equipment. Additionally, the elastomeric bushes are susceptible to wear and tear over time, especially in applications involving high temperatures, chemical exposure, or continuous heavy loads. This means that the bushes need to be replaced periodically to maintain the coupling's performance.
The performance of bushed couplings is influenced by several factors, including the material of the components, the design parameters, and the operating conditions. The torque capacity of a bushed coupling, for example, depends on the number and diameter of the pins, the material strength of the pins and hubs, and the shear strength of the elastomeric bushes. Increasing the number or diameter of the pins can increase the torque capacity, but this also increases the size and weight of the coupling. The misalignment capacity is determined by the flexibility of the bushes, with softer bushes able to accommodate greater misalignment but offering lower torque capacity. Harder bushes, on the other hand, have higher torque capacity but limited misalignment accommodation. Operating conditions such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals can also affect performance. High temperatures can cause the elastomeric bushes to harden or degrade, reducing their flexibility and lifespan. Chemical exposure can cause the bushes to swell, shrink, or break down, leading to coupling failure.
When selecting a bushed coupling for a specific application, several considerations must be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and reliability. First, the torque requirements of the application must be matched to the coupling's torque capacity. This involves calculating the maximum torque that the coupling will be required to transmit, which depends on the power of the driving motor and the speed of the shafts. Second, the type and magnitude of misalignment expected in the system must be considered. If the application involves significant angular or parallel misalignment, a coupling with more flexible bushes should be selected. Third, the operating speed of the shafts must be within the coupling's speed limit to avoid premature failure. Fourth, the operating environment, including temperature, humidity, and chemical exposure, must be considered when selecting the material of the bushes and hubs. For example, in high-temperature applications, synthetic rubber or polyurethane bushes should be used instead of natural rubber. Finally, the size and space constraints of the application must be taken into account, as some coupling variations are designed for compact spaces.
Advancements in material science and manufacturing technology have led to improvements in the performance and durability of bushed couplings. The development of high-performance elastomeric materials, such as reinforced rubber and advanced polyurethanes, has increased the torque capacity and temperature resistance of the bushes, expanding the range of applications for bushed couplings. Additionally, improvements in manufacturing processes, such as precision machining and injection molding, have resulted in more consistent component dimensions and better quality control, ensuring that bushed couplings perform reliably in critical applications. These advancements have also made it possible to produce custom bushed couplings tailored to specific application requirements, such as unique shaft sizes, torque capacities, or environmental conditions.
In conclusion, bushed couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, offering a simple, cost-effective, and versatile solution for connecting rotating shafts. Their ability to accommodate misalignment, dampen vibrations, and transmit torque efficiently makes them suitable for a wide range of applications across various industries. While they have certain limitations, such as lower operating speed and torque capacity compared to other coupling types, their advantages in terms of ease of installation, minimal maintenance, and vibration dampening make them a preferred choice for many low to medium speed, low to medium torque applications. By understanding the design, working principle, material selection, and performance characteristics of bushed couplings, industry professionals can select the right coupling for their specific application, ensuring optimal system performance, reliability, and longevity. As material science and manufacturing technology continue to advance, bushed couplings are likely to become even more versatile and reliable, further expanding their role in the ever-evolving field of mechanical engineering.
« Bushed Couplings » Update Date: 2026/1/10
URL: https://m.rokee.com/tags/bushed-couplings.html