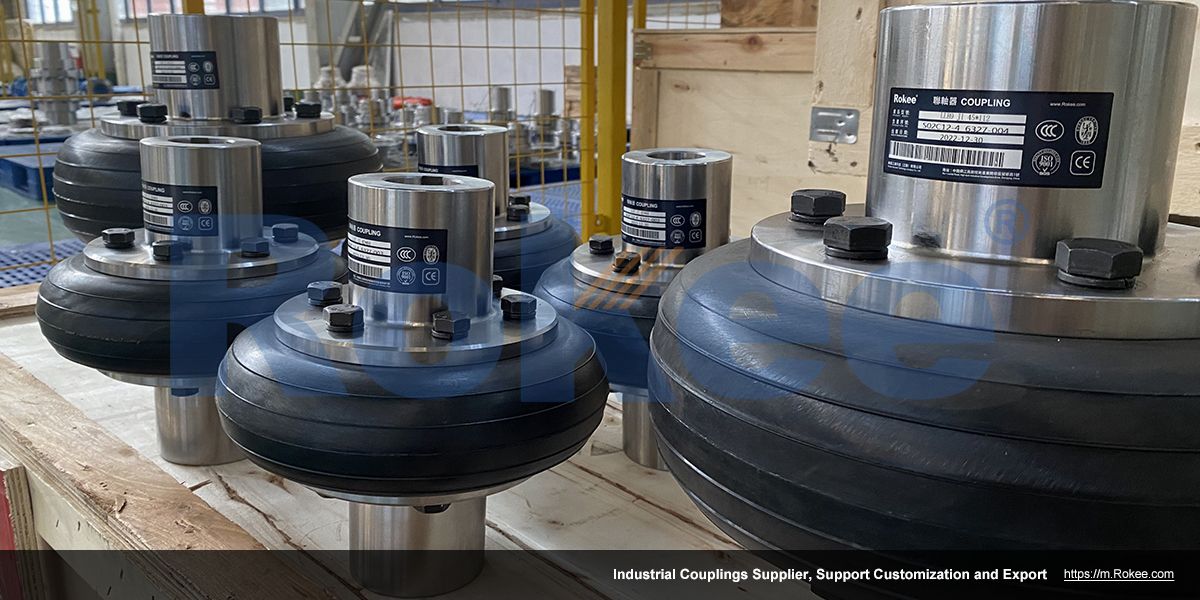
Rokee is a chinese Rubber Flexible Shaft Couplings Manufacturer, provide Rubber Flexible Shaft Couplings processing and customization services, Over the years, with excellent quality, we have been continuously providing many coupling products of various categories and uses complying with multiple standards and a full range of services, from the Rubber Flexible Shaft Couplings selection to final installation and operation, for the industry fields of ferrous metallurgy, nuclear power, gas turbine, wind power, ropeway construction, lifting transportation, general equipment, etc. We strictly comply with quality system requirements and implement the whole process control to become a reliable and trustworthy partner of customers.
Providing customers with better Rubber Flexible Shaft Couplings is always our driving force. Our aim is to transmit power for you and generate value for both of us. We look forward to joining you and becoming your partner for common progress.
-
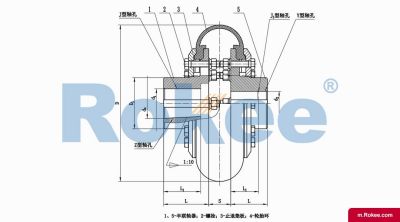
LLA Tyre Coupling
The LLA Tyre Coupling uses two semi-couplings to connect both sides of the elastic tyre body through internal pressing plates and bolts, making it easy to replace the elastic tyre body. The LLA Tyre Coupling is a kind of high elastic coupling, with good damping buffer and superior offset compensation performance.The working temperature of 20~80 degrees Celsius, transmitting torque 10~20000NM, suitable for damp, dust, shock, vibration, reversing the changeable and frequent starting working conditions, and convenient assembly and disassembly, no lubrication, durable and reliable. Non standard couplings are made in accordance with special needs. In overloading work and half coupling, there will be no malignant accidents.View More -
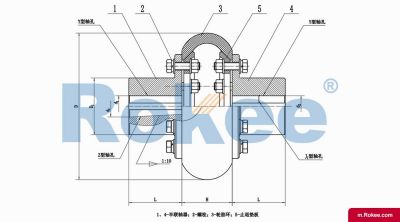
LLB Tyre Coupling
The LLB Tyre Coupling is a kind of high elastic coupling, with good damping buffer and superior offset compensation performance. The working temperature of 20~80 degrees Celsius, transmitting torque 10~20000NM, suitable for damp, dust, shock, vibration, reversing the changeable and frequent starting working conditions, and convenient assembly and disassembly, no lubrication, durable and reliable. Non standard couplings are made in accordance with special needs. In overloading work and half coupling, there will be no malignant accidents.View More -
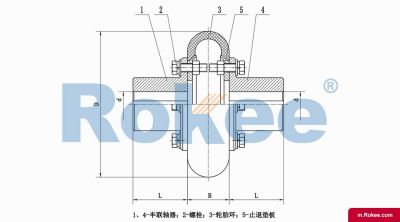
UL Tyre Coupling
UL Tyre Coupling adopts the structure of vulcanizing and bonding the tyre body with the metal connecting plate with threaded holes, which is then directly connected to the two semi-couplings by bolts for torque transmission and other displacement compensation.UL Tyre Couplings are flexible shaft coupling. UL type tire has good buffering performance. Operating temperature: -20~+80℃. Torque range: 10~25000N.M.UL Tyre Coupling mainly used in damp, dusty, vibration working environment. Because the elastic part is the whole tire, so, easy to disassemble and assemble. No lubrication is required.View More
Rubber flexible shaft coupling is a mechanical transmission device designed with a special elastic structure to compensate for the relative displacement between two shafts, and belongs to an important category of flexible shaft couplings with elastic elements. The core feature of this type of coupling is the high elastic deformation ability of rubber material, which can effectively adjust the axial, radial, and angular deviations of the connecting shaft system, significantly reduce the vibration amplitude of the transmission system, absorb impact energy, and improve the dynamic performance of the shaft system.
In the field of industrial transmission, rubber flexible shaft couplings play an irreplaceable role. Compared to metal elastic element couplings, rubber couplings have superior damping characteristics and can better suppress vibration and noise; Compared with flexible shaft couplings without elastic components, it also has buffering and shock-absorbing functions, which can protect the transmission system from damage caused by impact loads. According to industry statistics, the application proportion of rubber flexible shaft couplings in transmission systems with medium torque (50-8000N · m) is over 40%, especially in harsh working conditions such as dust and moisture.
The working principle of rubber flexible shaft couplings is based on elastic mechanics and vibration theory. When the active shaft transmits torque, the rubber components in the coupling undergo controllable elastic deformation, which can adapt to the relative displacement between the two shafts and dissipate vibration energy through internal friction of the material. Its working process simultaneously achieves three key functions: transmitting motion and power, compensating for axis deviation, and buffering and shock absorption. It is worth noting that the force transmission mechanism of different types of rubber couplings also varies, mainly including two basic modes of action: compression type (such as plum blossom elastic couplings) and shear type (such as tire type couplings).
The structural design of rubber flexible shaft couplings cleverly combines the reliability of mechanical transmission with the flexibility of elastic materials, forming a variety of distinctive configurations. A typical structural composition includes three main parts: metal wheels, rubber elastomers, and connecting components. Metal wheels are usually made of high-quality steel, aluminum alloy, or cast iron, and are responsible for connecting with the drive shaft and transmitting torque; Rubber elastomer is the core functional component, which is firmly bonded to metal parts through vulcanization process to form a complete structure; The connecting components include bolts, clamping devices, etc., to ensure the reliable connection of various parts of the coupling. This structural design enables rubber flexible shaft couplings to compensate for axial, radial, and angular deviations through elastic deformation of rubber components while transmitting torque. Generally speaking, the allowable axis offset can reach 3-5 times that of rigid couplings.
Compression type rubber coupling is one of the most common structural forms, represented by the plum blossom shaped elastic coupling. This type of coupling is equipped with a plum shaped rubber pad between the protrusions of two metal half couplings, which transmits torque and absorbs vibration through the compression deformation of the rubber. Its characteristics are compact structure, small axial size, and strong torque transmission ability. The compression type design allows rubber to mainly bear compressive stress when subjected to force, which is conducive to the high elasticity advantage of rubber. At the same time, the deformation of rubber is limited by metal claws, avoiding early damage caused by excessive deformation. The radial stiffness of compression type couplings is usually high, making them suitable for applications that require precise transmission of motion, such as servo drive systems.
Shear type rubber couplings adopt different force transmission mechanisms, with tire type couplings and U-shaped rubber couplings as typical representatives. In this type of design, rubber components mainly bear shear stress rather than compressive stress. For example, the rubber components of a tire type coupling are arranged in a circular shape, and when torque is transmitted, the rubber body undergoes shear deformation. The advantage of shear type design is that it can achieve greater elastic deformation, provide better vibration reduction effect, and have more balanced compensation ability in all directions. However, its torsional stiffness is generally low, and it may not perform as well as compression type couplings in situations where high-precision positioning is required. Shear type couplings are particularly suitable for working conditions with significant shaft deviation or strong vibration impact, such as ship propulsion systems, heavy engineering machinery, etc.
« Rubber Flexible Shaft Couplings » Post Date: 2024/5/6
URL: https://m.rokee.com/tags/rubber-flexible-shaft-couplings.html