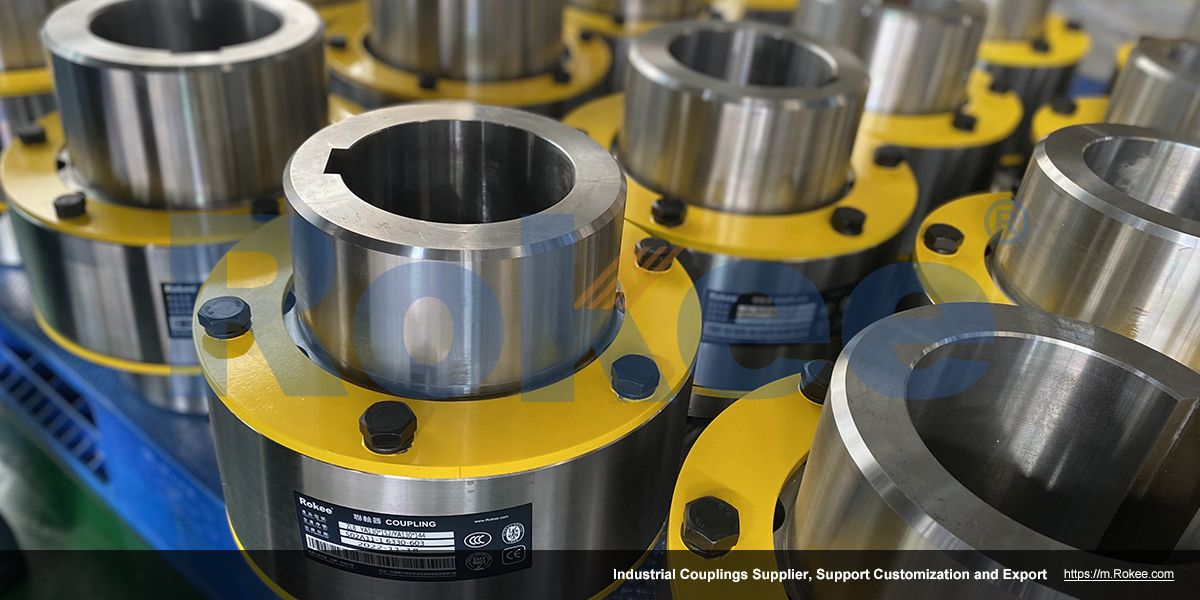
Rokee is a chinese Bush Pin Couplings Manufacturer, provide Bush Pin Couplings processing and customization services, Over the years, with excellent quality, we have been continuously providing many coupling products of various categories and uses complying with multiple standards and a full range of services, from the Bush Pin Couplings selection to final installation and operation, for the industry fields of ferrous metallurgy, nuclear power, gas turbine, wind power, ropeway construction, lifting transportation, general equipment, etc. We strictly comply with quality system requirements and implement the whole process control to become a reliable and trustworthy partner of customers.
Providing customers with better Bush Pin Couplings is always our driving force. Our aim is to transmit power for you and generate value for both of us. We look forward to joining you and becoming your partner for common progress.
-
LT/TL Elastic Sleeve Pin Coupling
LT Elastic Sleeve Pin Coupling is the basic form of this series of couplings.View More -
LTZ/TLL Elastic Sleeve Pin Coupling With Brake Wheel
LTZ Elastic Sleeve Pin Coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required.View More
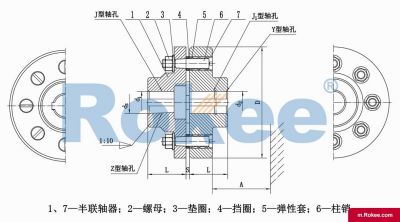
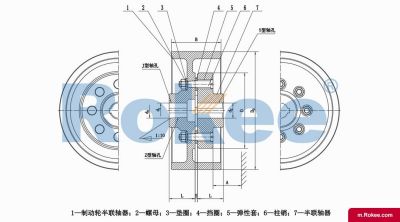
Bush Pin Coupling is a special type of coupling that combines the characteristics of a sleeve and a pin shaft, used to achieve connection and torque transmission between two shafts.
The Bush Pin Coupling is mainly composed of two half couplings, a pin shaft, and a bushing. Two half couplings are fixed on two shafts respectively, and the pin shaft passes through the corresponding holes of the two half couplings and is supported and positioned by a bushing. The bushing is usually installed between the pin shaft and the half coupling hole to reduce friction and wear, while ensuring the stable operation of the pin shaft.
The Bush Pin Coupling achieves torque transmission between two shafts through the coordination of the pin shaft and the bushing. When the driving shaft rotates, the pin shaft drives the driven shaft to rotate together, thereby achieving torque transmission. The presence of bushings reduces friction between the pin shaft and the half coupling hole, extending the service life of the coupling.
Characteristics and advantages
Strong load-bearing capacity: The Bush Pin Coupling has a high load-bearing capacity and is suitable for situations where large torque is transmitted.
Simple structure: Its structure is relatively simple, easy to install and maintain.
Strong adaptability: able to adapt to axial, radial, and angular displacements within a certain range, improving installation flexibility.
Good wear resistance: The use of bushings reduces friction and wear, improving the wear resistance of the coupling.
Bush Pin Couplings are widely used in various mechanical equipment, especially in situations where high torque transmission and heavy loads are required. For example, in transmission devices such as mixers, pumps, and fans, Bush Pin Couplings play an important role.
Precautions
Selection: When choosing a Bush Pin Coupling, it is necessary to select according to the actual working conditions and requirements to ensure that the bearing capacity and adaptability of the coupling meet the requirements.
Installation: During the installation process, it is necessary to maintain the coaxiality of the shaft and half coupling to avoid excessive deviation and vibration.
Maintenance: Regularly check the wear of the bushing and pin shaft, replace severely worn components in a timely manner, and ensure the normal operation of the coupling.
The Bush Pin Coupling is a type of coupling with a simple structure, strong load-bearing capacity, strong adaptability, and good wear resistance. In practical applications, it is necessary to select and maintain equipment according to specific working conditions and requirements to ensure its normal operation and efficient performance.
In the realm of mechanical power transmission, couplings serve as indispensable components that bridge rotating shafts, enabling the seamless transfer of torque while accommodating inevitable misalignments and mitigating operational vibrations. Among the diverse array of coupling types available, the bush pin coupling stands out as a cost-effective, versatile, and robust solution widely employed across numerous industrial sectors. Characterized by its simple construction, ease of installation, and ability to dampen shock loads, this type of flexible coupling has become a staple in applications ranging from small-scale motors to heavy-duty industrial machinery.
At its core, the bush pin coupling is a flexible coupling design that consists of several key components working in tandem to facilitate power transmission. The fundamental structure comprises two flanged hubs, often referred to as semi-couplings, which are designed to be mounted on the ends of the two shafts that require connection. Each hub is equipped with a series of evenly spaced holes around its flange circumference, these holes being the critical interface points for torque transfer. Inserted through these corresponding holes in the two hubs are metal pins, which are typically cylindrical in shape and secured in place using nuts and washers to ensure a firm fit. The defining feature of this coupling type is the presence of elastomeric bushes that line the holes in one of the hubs, acting as a buffer between the metal pins and the hub itself. These bushes, usually made from materials such as polyurethane, neoprene, or rubber, are responsible for the coupling’s flexibility and vibration-damping capabilities. In some specialized designs, additional components such as spacer sleeves may be incorporated to accommodate larger distances between the connected shafts, allowing for easier maintenance without the need to disassemble the entire shaft assembly. The simplicity of this structural design not only simplifies manufacturing and assembly processes but also contributes to the coupling’s reliability and cost-effectiveness, making it accessible for a wide range of industrial applications.
The working principle of a bush pin coupling revolves around the efficient transfer of torque through the interaction of its core components, while leveraging the flexibility of the elastomeric bushes to address misalignments and vibrations. When torque is applied to one of the connected shafts, it is first transmitted to the corresponding hub, which then transfers this rotational force to the metal pins inserted through its flange holes. The pins, in turn, exert pressure on the elastomeric bushes, which are in contact with the second hub. Through the deformation and resilience of the bush material, the torque is smoothly transmitted to the second hub and ultimately to the driven shaft. A key aspect of this working mechanism is the ability of the elastomeric bushes to accommodate various types of shaft misalignment, including parallel misalignment (where the shafts are offset horizontally), angular misalignment (where the shafts are not collinear and form an angle), and axial misalignment (where the shafts move along their axial direction). As the shafts rotate, the bushes compress and expand in response to these misalignments, ensuring that the torque transfer remains consistent without imposing excessive stress on the shafts or other connected components. Additionally, the elastomeric material of the bushes acts as a shock absorber, dampening the impact loads that may occur during startup, shutdown, or sudden changes in operational load. This shock-damping capability not only protects the coupling components themselves but also extends the lifespan of the connected machinery by reducing the transmission of harmful vibrations.
The selection of materials for bush pin coupling components is a critical process that directly influences the coupling’s performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. The choice of materials is primarily driven by factors such as the operational torque and speed, the nature of the load (steady or intermittent, shock or vibration-prone), environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, corrosive elements), and cost considerations. For the metal hubs (semi-couplings) and pins, materials with high tensile strength, toughness, and wear resistance are preferred to withstand the mechanical stresses imposed during torque transmission. Common materials used for these components include cast iron, carbon steel, and alloy steels such as SAE 8620, which offers enhanced toughness and wear resistance compared to standard carbon steels like AISI 1020. Cast iron is often chosen for lighter-duty applications due to its cost-effectiveness and good machinability, while carbon steel and alloy steels are employed for medium to heavy-duty applications where higher strength and durability are required. In some cases, through-hardened steels with tempered martensite microstructures may be used for the hubs or pins to further improve tensile strength, particularly in applications involving overloaded conditions.
The elastomeric bushes, being the flexible and vibration-damping element of the coupling, require materials that exhibit excellent resilience, good resistance to wear and tear, and the ability to withstand the operational temperature range of the application. Polyurethane is a popular choice for bush materials due to its high load-bearing capacity, excellent abrasion resistance, and good resistance to oils and chemicals. Neoprene, another commonly used material, offers superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and extreme temperatures, making it suitable for outdoor or harsh environmental applications. Rubber bushes, while more economical, may have lower durability and load-bearing capacity compared to polyurethane or neoprene, making them ideal for light-duty, low-speed applications. The selection of the bush material is also influenced by the desired level of flexibility and damping; softer materials provide greater vibration dampening but may have lower torque-carrying capacity, while harder materials can transmit higher torques but offer reduced flexibility. It is essential to match the bush material to the specific operational requirements to ensure optimal coupling performance and longevity.
Bush pin couplings exhibit a set of operational characteristics that make them particularly suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. One of their most notable features is their torsional flexibility, which allows for the accommodation of minor shaft misalignments typically up to 0.5 degrees angular misalignment and small parallel misalignments. This flexibility eliminates the need for precise shaft alignment during installation, reducing installation time and costs. Another key operational characteristic is their maintenance-free nature, primarily due to the absence of lubrication requirements. Unlike gear or chain couplings, which require regular lubrication to prevent wear and ensure smooth operation, the elastomeric bushes of bush pin couplings do not need lubrication, simplifying maintenance routines and reducing operational costs. Additionally, the modular construction of many bush pin coupling designs allows for easy replacement of worn components, such as the bushes or pins, without the need to disassemble the entire coupling or remove the hubs from the shafts. This ease of maintenance minimizes downtime, which is crucial for industrial operations where continuous productivity is essential.
The operational speed and torque capacity of bush pin couplings vary depending on their size, material selection, and design configuration. In general, these couplings are well-suited for low to medium speed applications, with operating speeds typically lower than those of gear or chain couplings due to the flexible nature of the elastomeric bushes. However, advancements in material technology have allowed for the development of bush pin couplings capable of handling higher speeds for specific applications. The torque capacity of bush pin couplings ranges from relatively low values for small-scale applications to very high values exceeding 1,200,000 Nm for heavy-duty industrial drives, with bore diameters ranging from 11 mm to 600 mm to accommodate different shaft sizes. The ability to handle a wide range of torque capacities makes bush pin couplings versatile enough to be used in applications ranging from small pumps and fans to large conveyors and crane drives. It is important to note that the operational efficiency of bush pin couplings is slightly lower than that of rigid couplings or gear couplings due to the friction and deformation of the elastomeric bushes during torque transmission. However, this slight reduction in efficiency is often offset by the coupling’s other advantages, such as vibration damping, misalignment accommodation, and low maintenance requirements.
The versatility and robustness of bush pin couplings make them suitable for a diverse range of industrial applications across various sectors. In the manufacturing industry, they are widely used in machinery such as conveyors, pumps, compressors, mixers, and screens. Conveyor systems, which are essential for material handling in factories, warehouses, and mining operations, benefit greatly from the coupling’s ability to accommodate misalignments and dampen vibrations, ensuring continuous and reliable operation even in harsh working conditions. Pumps and compressors, which operate at varying speeds and loads, rely on the coupling’s flexibility to absorb shock loads and reduce vibration, protecting the pump or compressor components from premature wear. In the construction sector, bush pin couplings are employed in heavy-duty equipment such as cranes, excavators, and concrete mixers. These applications require couplings that can withstand high torque loads and harsh environmental conditions, and the robust construction of bush pin couplings, combined with their shock-damping capabilities, makes them an ideal choice. Cranes, in particular, benefit from the coupling’s ability to handle sudden load changes and misalignments that occur during lifting operations.
The transportation and automotive sectors also utilize bush pin couplings in various applications. In the automotive industry, they are used in drive shafts, gearboxes, and steering systems, where their vibration-damping capabilities contribute to improved vehicle performance and driving comfort. Marine applications, which involve harsh environmental conditions such as saltwater corrosion and high vibration, rely on bush pin couplings for power transmission in propulsion systems, generators, and auxiliary machinery. The corrosion-resistant materials used in the construction of marine-grade bush pin couplings ensure reliable performance even in these challenging environments. The renewable energy sector, including wind turbines and solar power plants, is another area where bush pin couplings find application. Wind turbines, which are subject to dynamic loads and torque variations due to wind speed fluctuations, benefit from the coupling’s ability to accommodate misalignments and dampen vibrations, ensuring the efficient transfer of energy from the turbine to the generator. Agricultural machinery, such as tractors, harvesters, and irrigation systems, also uses bush pin couplings to transmit power between shafts, facilitating the mechanized processes essential for modern farming practices.
Like any mechanical component, bush pin couplings have their advantages and limitations that must be considered when selecting them for a specific application. One of the primary advantages is their cost-effectiveness; the simple design and readily available materials make them more affordable than many other types of couplings, such as disc or gear couplings. Their ease of installation and maintenance is another significant advantage, requiring minimal specialized tools or expertise. The vibration-damping and shock-absorbing capabilities of the elastomeric bushes protect the connected machinery from damage, extending the overall lifespan of the system. Additionally, their ability to accommodate multiple types of misalignments eliminates the need for precise alignment, reducing installation time and costs. The maintenance-free nature of most bush pin couplings, due to the absence of lubrication requirements, further reduces operational costs and downtime.
Despite their numerous advantages, bush pin couplings also have certain limitations. As mentioned earlier, their operational speed is generally lower than that of gear or chain couplings, making them less suitable for high-speed applications. The elastomeric bushes are subject to wear and fatigue over time, especially in applications involving high temperatures, harsh chemicals, or continuous heavy loads. This wear can lead to reduced flexibility and vibration-damping capabilities, eventually requiring component replacement. The torque capacity of bush pin couplings, while sufficient for most medium-duty applications, may be insufficient for extremely high-torque applications where gear or disc couplings would be more appropriate. Additionally, the elastomeric materials used in the bushes may degrade over time due to environmental factors such as ozone, UV radiation, or exposure to oils and chemicals, limiting their lifespan in certain environments. It is important to consider these limitations when selecting a bush pin coupling, ensuring that it is compatible with the specific operational requirements of the application.
Proper maintenance and inspection are essential to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of bush pin couplings. While these couplings are generally maintenance-free, regular inspections can help identify potential issues before they lead to equipment failure. Routine inspections should include checking for wear or damage to the elastomeric bushes, such as cracks, tears, or excessive deformation. Worn bushes should be replaced promptly to maintain the coupling’s flexibility and vibration-damping capabilities. The metal pins, nuts, and washers should also be inspected for signs of wear, corrosion, or loosening. Loose nuts should be tightened to ensure a secure fit, while corroded or worn pins should be replaced to prevent torque transmission issues. The hubs should be checked for cracks or deformation, particularly in areas around the flange holes where stress concentrations are highest.
In addition to visual inspections, it is important to monitor the operational performance of the coupling. Unusual noises, such as squeaking or rattling, may indicate worn or damaged bushes. Increased vibration or misalignment may also be a sign of coupling wear. Regular measurement of shaft alignment can help identify any changes that may affect the coupling’s performance. When replacing components, it is essential to use parts that are compatible with the original coupling design, including the correct material and size of bushes and pins. In applications involving harsh environments, such as high temperatures or corrosive substances, selecting bush materials that are resistant to these conditions can extend the coupling’s lifespan. Proper storage of replacement parts, particularly elastomeric bushes, is also important to prevent degradation before installation. Bushes should be stored in a cool, dry environment away from direct sunlight and chemicals.
In conclusion, bush pin couplings are a vital component in modern mechanical power transmission systems, offering a cost-effective, versatile, and reliable solution for connecting rotating shafts. Their simple yet effective design, combined with the flexibility and vibration-damping capabilities of the elastomeric bushes, makes them suitable for a wide range of applications across numerous industrial sectors. The careful selection of materials for the hubs, pins, and bushes ensures that the coupling can withstand the specific operational requirements of the application, whether it be low-speed light-duty or high-torque heavy-duty. While they have certain limitations, such as lower operational speeds and potential wear of elastomeric components, their advantages far outweigh these drawbacks in most applications. Proper maintenance and inspection further enhance their performance and longevity, ensuring that they continue to contribute to the efficient and reliable operation of mechanical systems. As industrial technology continues to advance, the design and material technology of bush pin couplings are likely to evolve, further expanding their range of applications and improving their performance. Whether in manufacturing, construction, transportation, or renewable energy, bush pin couplings will remain an indispensable part of mechanical power transmission for years to come.
« Bush Pin Couplings » Update Date: 2026/1/10
URL: https://m.rokee.com/tags/bush-pin-couplings.html