Rokee is a chinese Telescopic Universal Joints Manufacturer, provide Telescopic Universal Joints processing and customization services, Over the years, with excellent quality, we have been continuously providing many coupling products of various categories and uses complying with multiple standards and a full range of services, from the Telescopic Universal Joints selection to final installation and operation, for the industry fields of ferrous metallurgy, nuclear power, gas turbine, wind power, ropeway construction, lifting transportation, general equipment, etc. We strictly comply with quality system requirements and implement the whole process control to become a reliable and trustworthy partner of customers.
Providing customers with better Telescopic Universal Joints is always our driving force. Our aim is to transmit power for you and generate value for both of us. We look forward to joining you and becoming your partner for common progress.
-
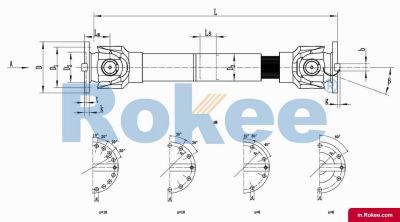
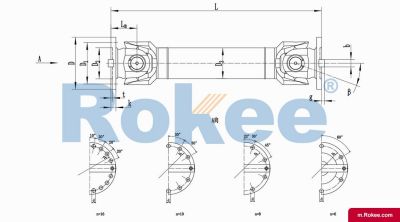
SWC-BH Cardan Shaft
SWC-BH standard telescopic welded universal joint couplingView More -
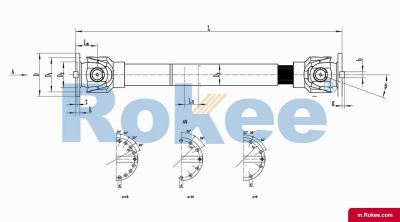
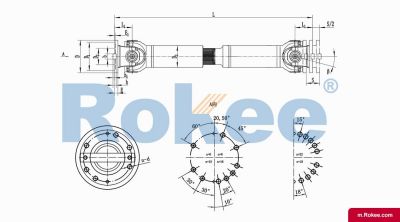
SWC-CH Cardan Shaft
SWC-CH long telescopic welded universal joint couplingView More -
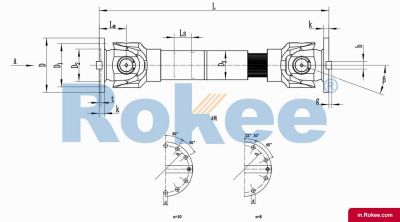
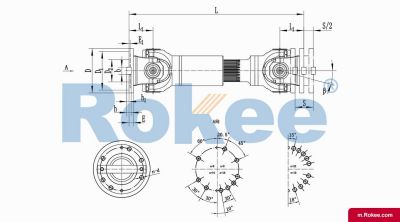
SWC-DH Cardan Shaft
SWC-DH short telescopic welded universal joint couplingView More -
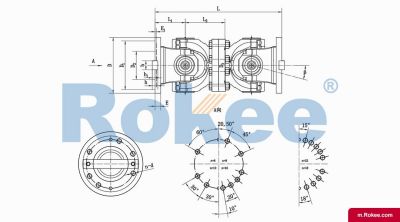
SWC-WD Cardan Shaft
SWC-WD non-telescopic short universal joint couplingView More -
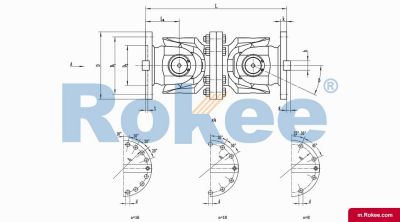
SWC-WH Cardan Shaft
SWC-WH non-telescopic welded universal joint couplingView More -
SWP-A Cardan Shaft
SWP-A telescopic long type universal joint couplingView More -
SWP-B Cardan Shaft
SWP-B telescopic short type universal joint couplingView More -
SWP-C Cardan Shaft
SWP-C non telescopic short type universal joint couplingView More -
SWP-D Cardan Shaft
SWP-D non telescopic long type universal joint couplingView More
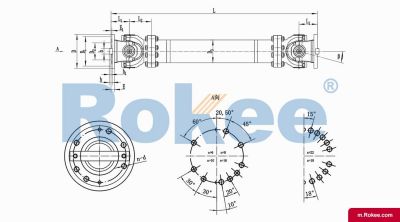
A telescopic universal joint is a mechanical coupling device that integrates axial telescopic function and universal transmission characteristics. It can reliably transmit torque and rotational motion between two shafts with relative position changes. This type of universal joint not only allows for significant angular deviation between the two connected shafts (usually up to 15 ° -47 °), but also compensates for axial displacement through its own telescopic structure, with displacement compensation ranging from a few millimeters to one meter, depending on design and application requirements.
Compared with traditional universal joints, the most significant feature of telescopic universal joints is their dual compensation capability. On the one hand, like all universal joints, it can adapt to the angular deviation between two connected shafts; On the other hand, its built-in telescopic mechanism (usually a spline or sleeve structure) allows for changes in axial length, which gives it significant advantages in the following areas:
Installation flexibility: During equipment assembly, there is no need for extremely high alignment accuracy, reducing installation difficulty and labor costs.
Adaptability to working conditions: It can automatically compensate for changes in axial position caused by vibration, thermal expansion, or foundation settlement during equipment operation.
System reliability: By absorbing displacement and vibration, it protects connected equipment from excessive stress and extends the service life of the entire transmission system.
Space utilization: Compared to the combination of fixed universal joints and sliding couplings, the telescopic universal joint structure is more compact and saves installation space.
It is precisely because of these advantages that telescopic universal joints have become an important choice in modern mechanical transmission design, playing a key role in many industrial fields. With the advancement of materials science and manufacturing technology, its performance parameters and application scope are still constantly expanding.
The reason why the telescopic universal joint can simultaneously achieve angle compensation and axial displacement compensation is attributed to its carefully designed internal structure. Different types of telescopic universal joints have differences in specific construction, but they are generally composed of two main parts: the universal transmission mechanism and the axial telescopic mechanism, which are organically integrated to form a fully functional whole.
Cross axis telescopic universal joint is one of the most common types, with a relatively simple structure but very effective. This universal joint consists of two main parts: the universal joint body and the telescopic sleeve. The universal joint body adopts a traditional cross axis structure, including two fork shaped joints and a cross axis. Needle roller bearings are installed on the four necks of the cross axis to reduce friction. This design allows for a significant angular deviation between two connected axes, typically up to 15 ° -25 °. The telescopic function is achieved through an internal and external spline pair, with the internal spline shaft and external spline sleeve precisely matched to transmit torque and allow axial sliding. Lubricating grease fittings and sealing devices are usually installed at the spline mating area to ensure long-term lubrication needs and prevent contaminants from entering.
When power is transmitted from the drive shaft to the telescopic universal joint, torque is transmitted through the following path: for the cross shaft type, torque is transmitted to the cross shaft through the universal joint fork at the input end, and then transmitted to the universal joint fork at the output end through the cross shaft; For cage type, torque is transmitted through the engagement of steel balls between the inner and outer raceways. During this process, if there is an angle deviation between the two connected axes, the cross axis will deflect accordingly or the steel ball will adjust its position within the raceway to achieve angle compensation.
When the distance between the axes of connected devices changes due to thermal expansion, vibration, or changes in installation position, the telescopic mechanism begins to function. In a cross axis universal joint, the internal spline shaft will slide axially relative to the external spline sleeve; In the cage type universal joint, there will be axial relative movement between the star shaped sleeve and the cylindrical shell. This axial displacement does not affect the transmission of torque, but can effectively release the axial stress caused by changes in shaft spacing, protecting bearings and other transmission components from excessive additional loads.
It is worth mentioning that modern high-performance telescopic universal joints are often made of high-quality alloy steel, such as 42CrMo, and undergo quenching and tempering heat treatment and precision machining to ensure sufficient strength and wear resistance. Special coating or surface treatment techniques may also be used on key friction pairs such as key tooth surfaces and raceway surfaces to further reduce the friction coefficient and extend their service life. Sealing technology is also constantly advancing, and the application of multi lip sealing rings or composite sealing structures enables universal joints to maintain good lubrication in harsh environments such as high dust and high humidity.
The cross axis telescopic universal joint is the most traditional and common type, with a relatively simple structure consisting of two universal joint forks, a cross axis, and needle roller bearings, and integrated with a spline telescopic mechanism. The main advantages of this universal joint are its sturdy structure, strong load-bearing capacity, and low manufacturing cost, making it particularly suitable for transmitting large torque. Widely used in heavy-duty trucks, construction machinery, and industrial transmission systems. For example, in the transmission shaft system of commercial vehicles, the cross axis telescopic universal joint can effectively compensate for the changes in wheelbase and angle deviation caused by the rear axle suspension movement, while bearing the huge torque output by the engine.
However, the cross axis universal joint also has some inherent drawbacks. The main problem is transmission non-uniformity - when there is an angle between the two axes, the angular velocity of the output shaft will produce periodic fluctuations, which intensify with the increase of the angle. Therefore, in practical applications, double cross axis universal joints are often used in pairs, and specific arrangements are made to counteract this speed fluctuation. In addition, the allowable deflection angle of the cross axis universal joint is relatively small (generally not exceeding 25 °), which may not be suitable for situations that require large angle transmission. The typical WSS type telescopic universal joint belongs to this category, which allows the angle between two axes to reach 45 °, the axial expansion and contraction can reach 1000mm, the rated torque can reach 2000N · m, and the high-speed model can reach 4000rpm.
« Telescopic Universal Joints » Post Date: 2024/5/6
URL: https://m.rokee.com/tags/telescopic-universal-joints.html